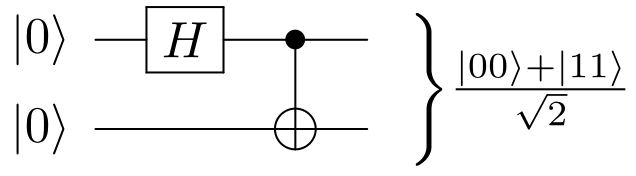
One of the four following states:
The Bell states are entangled and non-separable. Intuitively, we can see that when we measure that state, the values of the first and second bit are strictly correlated. This is the hallmark of quantum computation: making up states where qubits are highly correlated to match a specific algorithmic answer, and opposed to uniformly random noise. For example, the Bell state circuit is a common hello world, e.g. it is used in the official Qiskit hello world.
In Qiskit at: qiskit/hello.py.
Quantum circuit that generates the Bell state
. Source. TODO clear example and application.
www.quantamagazine.org/quantum-memory-proves-exponentially-powerful-20241016/ from Quanta Magazine has an incomprehensible news of something that sounds cool
Articles by others on the same topic
A quantum state is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics that describes the state of a quantum system. It encapsulates all the information about the system and can be represented in several ways, such as: 1. **Wave Function**: In non-relativistic quantum mechanics, a quantum state can be represented by a wave function, usually denoted by the Greek letter psi (Ψ).