In order to solve conflicts, you just have to understand what commit you are trying to move where.
E.g. if from:we do:what happens step by step is first 6 is moved on top of 5:and then 7 is moved on top of the new 6:
5 master
|
4 7 my-feature HEAD
| |
3 6
|/
2
|
1git rebase master6on5 HEAD
|
5 master
|
4 7 my-feature
| |
3 6
| |
2-----------------+
|
17on5 HEAD
|
6on5
|
5 master
|
4 7 my-feature
| |
3 6
| |
2-----------------+
|
17on5 my-feature HEAD
|
6on5
|
5 master
|
4
|
3
|
2
|
1The key to solve conflicts is:
You have to understand what are the two commits that touched a given line (one from master, one from features), and then combine them somehow.
Or in other words, at every rebase conflict we have something like:Therefore there are 2 diffs that you have to understand and reconcile:
master-commit feature-commit
| |
| |
base-commit------+
|
|base-committomaster-commitbase-committofeature-commit
diff3 conflict is basically what you always want to see, either by setting it as the default as per stackoverflow.com/questions/27417656/should-diff3-be-default-conflictstyle-on-git:git config --global merge.conflictstyle diff3git checkout --conflict=diff3With this, conflicts now show up as:
++<<<<<<< HEAD
+5
++||||||| parent of 7b0f59d (6)
++3
++=======
+ 6
++>>>>>>> 7b0f59d (6)7b0f59d is the SHA-2 of commit 6.instead of the inferior default:
++<<<<<<< ours
+5
++=======
+ 6
++>>>>>>> theirsWe can also observe the current tree state during resolution:so we understand that we are now at 5 and that we are trying to apply our commit
* b4ec057 (HEAD, master) 5
* 0b37c1b 4
| * fbfbfe8 (my-feature) 7
| * 7b0f59d 6
|/
* 661cfab 3
* 6d748a9 2
* c5f8a2c 16So it is much clearer what is happening:and so now we have to decide what the new code is that will put both of these together.
We now reach:and the tree looks like:So we understand that:
++<<<<<<< HEAD
+11
++||||||| parent of fbfbfe8 (7)
++6
++=======
+ 7
++>>>>>>> fbfbfe8 (7)* ca7f7ff (HEAD) 6
* b4ec057 (master) 5
* 0b37c1b 4
| * fbfbfe8 (my-feature) 7
| * 7b0f59d 6
|/
* 661cfab 3
* 6d748a9 2
* c5f8a2c 1and after resolving that one we now reach:
* e1aaf20 (HEAD -> my-feature) 7
* ca7f7ff 6
* b4ec057 (master) 5
* 0b37c1b 4
* 661cfab 3
* 6d748a9 2
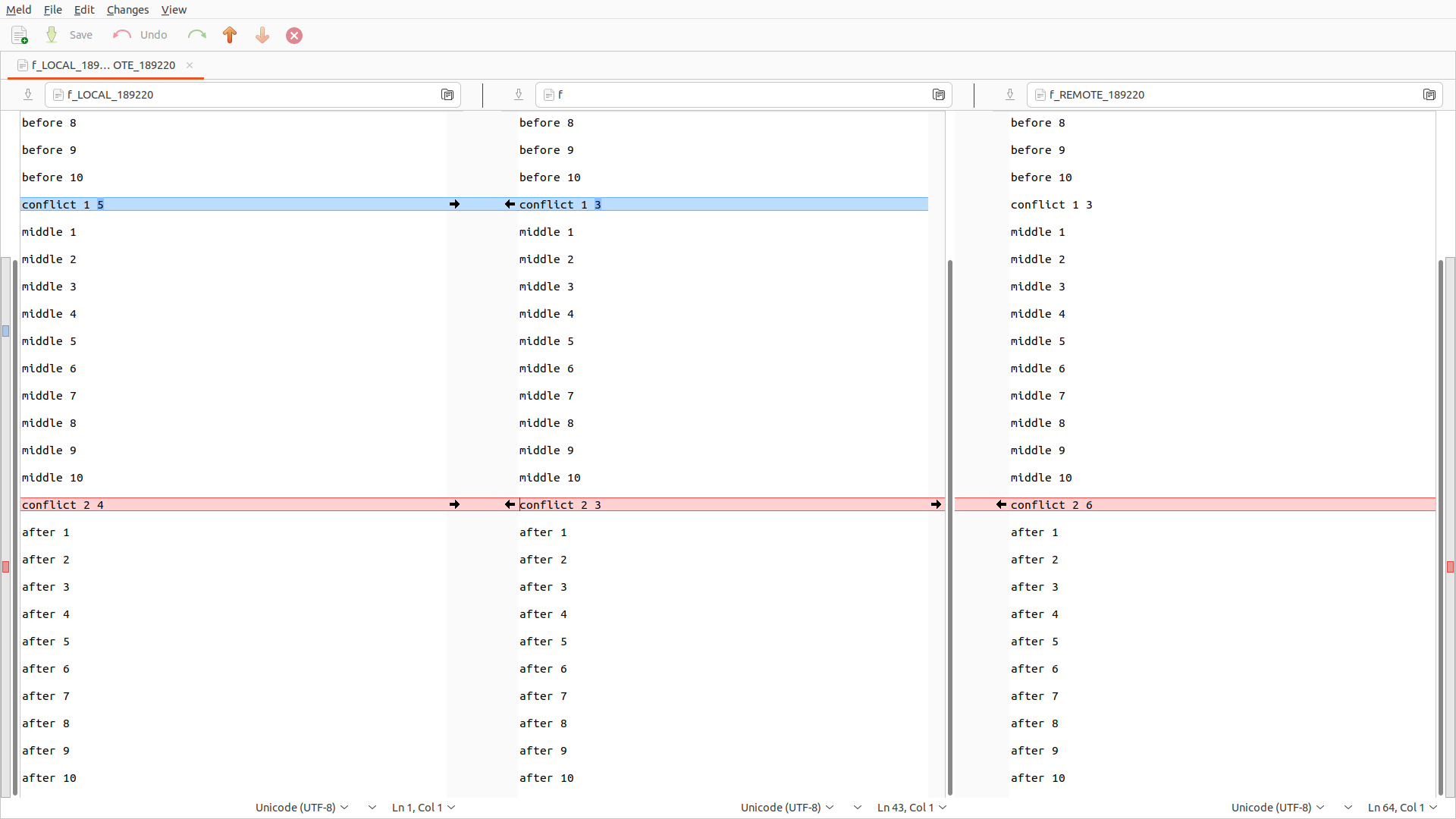
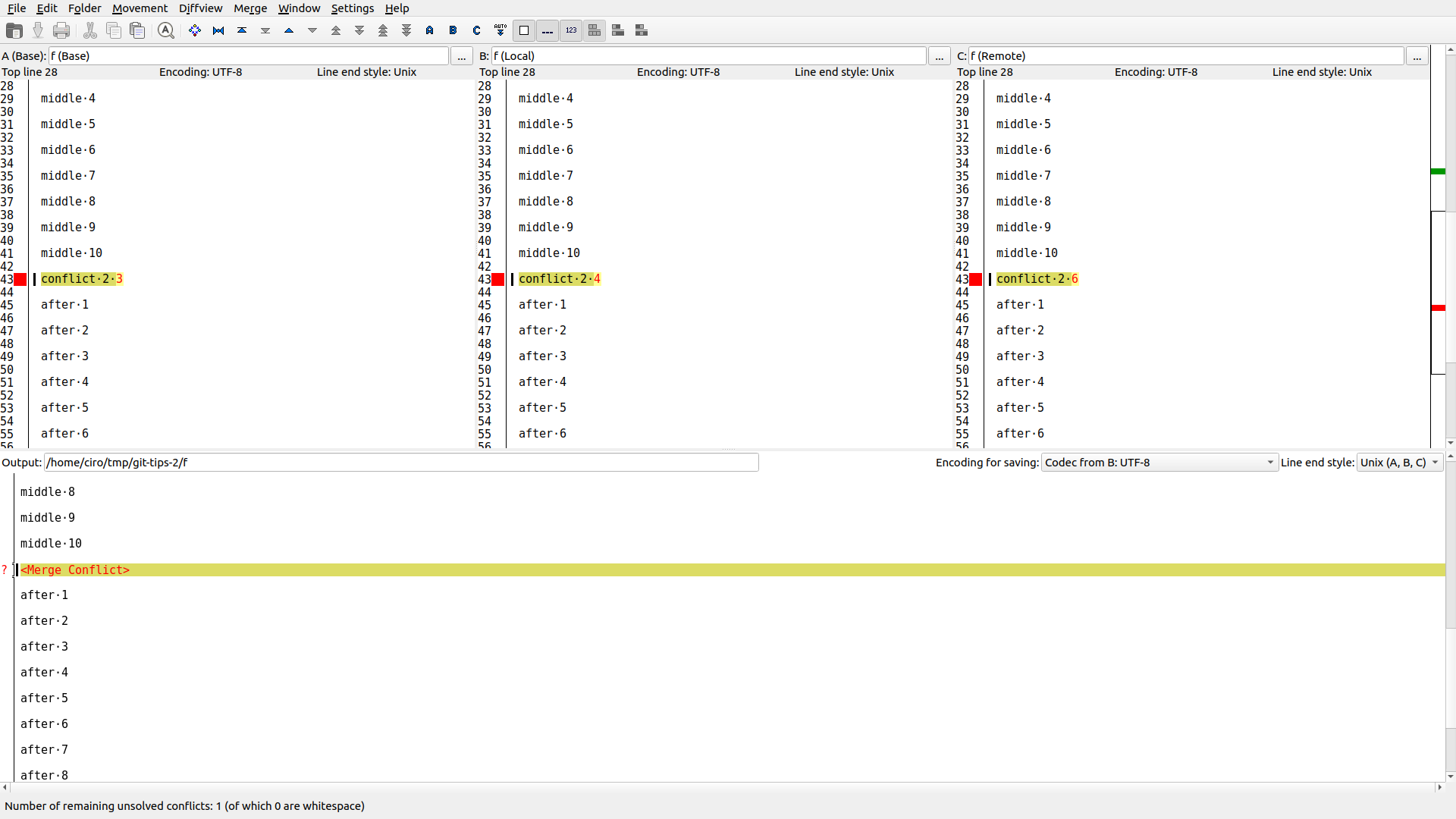
* c5f8a2c 1These are good free newbie GUI options:
sudo apt install meld
git mergetool --tool meld
sudo apt install kdiff3
git mergetool --tool kdiff3git-tips-2.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -eux
add() (
rm -f f
for i in `seq 10`; do
printf "before $i\n\n" >> f
done
printf "conflict 1 $1\n\n" >> f
for i in `seq 10`; do
printf "middle $i\n\n" >> f
done
printf "conflict 2 $2\n\n" >> f
for i in `seq 10`; do
printf "after $i\n\n" >> f
done
git add f
)
rm -rf git-tips-2
mkdir git-tips-2
cd git-tips-2
git init
for i in 1 2 3; do
add $i $i
git commit -m $i
done
add 3 4
git commit -m 4
add 5 4
git commit -m 5
git checkout HEAD~2
git checkout -b my-feature
add 3 6
git commit -m 6
add 7 6
git commit -m 7git rebase does not tell you that, and that sucks.We only know which commit from the feature branch caused the problem.
Generally we can guess or it is not needed, but
imerge does look promising: stackoverflow.com/questions/18162930/how-can-i-find-out-which-git-commits-cause-conflicts Articles by others on the same topic
There are currently no matching articles.