Capgemini Created 2025-07-01 Updated 2025-07-16
Atos Created 2025-07-01 Updated 2025-07-16
Anthropic Created 2025-07-01 Updated 2025-07-16
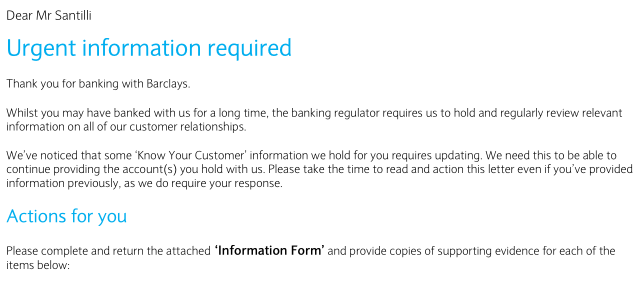
Sponsor Ciro Santilli's work on OurBigBook.com 1000 Monero donation Barclays regulation round 2 Created 2025-07-01 Updated 2025-09-09
On the 20th of June 2025, Barclays sent another request for information repeating a few of the items from last time without clear justification of what was wrong with the previous information.
Ciro quickly printed out the documents, but didn't know where to send them to, and had to wait until the 2nd of July for the return envelope to arrive, which he sent back on the 4th of July.
Announcements:
On the 28th of July 2025, Barclays finally replied with a hopefully final (who knows, everything is such a mess with this process):So Ciro Santilli gets to keep his account and the anonymous ~80k cashed out to it, but he cannot receive further anonymous donations on it.
Following a review of the above account, we have identified large value crypto assets with unknown sources. If such activity continues, keeping this account open poses a risk that we might breach laws or regulations. We therefore request that such payments are halted and, if the transactions repeat, we will take action to close this account with immediate notice. In the event of any closure, you will be required to repay any overdraft or other borrowing on the account.
As an outcome of this, I've also had to update my donation guidelines to not count anonymous donations towards my goals.
Barclays regulation felt so sloppy that I'm sure that with some effort to essentially launder the money, e.g. cashing out smaller amounts across various accounts, which I explicitly did not do in part to test the system, I would have gotten away with it, or large part of it. But I'm not going to be the one put this theory to the test.
Announcements:
- www.quora.com/Is-it-legal-for-billionaires-to-make-anonymous-charitable-donations-How-can-it-be-determined-if-a-large-sum-of-money-was-donated-anonymously-or-not/answer/Ciro-Santilli
- x.com/cirosantilli/status/1953780424242548749
- mastodon.social/@cirosantilli/114992839094805850
- www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:share:7359544588732178434/
HybridMedical Created 2025-07-01 Updated 2025-07-16
Must be closely related to XVIVO et al.
Quantum Information course of the University of Oxford Hilary 2023 1 1 a Created 2025-06-17 Updated 2025-07-16
Quantum Information course of the University of Oxford Hilary 2023 1 1 Created 2025-06-17 Updated 2025-07-16
Quantum Information course of the University of Oxford Hilary 2023 1 Created 2025-06-17 Updated 2025-07-16
Quantum Information course of the University of Oxford Hilary 2023 Problem sheet Created 2025-06-17 Updated 2025-07-16
CPU functional unit Created 2025-06-17 Updated 2025-07-16
AMD 7840U Created 2025-06-17 Updated 2025-07-16
Cavendish Professor of Physics Created 2025-06-17 Updated 2025-07-16
As beautifully put in The Eighth Day of Creation:
For more than a hundred years, the Cavendish Professorship has been the chair of experimental physics in the University of Cambridge. The man in that chair rules the university's research in physics. Indeed, for most of that hundred years the Cavendish Professor was preeminent in British science, with an authority that made him, as it were, the archbishop of physics
Intel i7-7820HQ Created 2025-06-17 Updated 2025-07-16
Superscalar processor Created 2025-06-17 Updated 2025-07-16
University of Cambridge alumnus Created 2025-06-17 Updated 2025-07-16
Professorship of the university of Cambridge Created 2025-06-17 Updated 2025-07-16
Intel CPU Created 2025-06-17 Updated 2025-07-16
C-peptide Created 2025-06-17 Updated 2025-07-16
B chain of insulin Created 2025-06-17 Updated 2025-07-16
A chain of insulin Created 2025-06-17 Updated 2025-07-16
Unlisted articles are being shown, click here to show only listed articles.