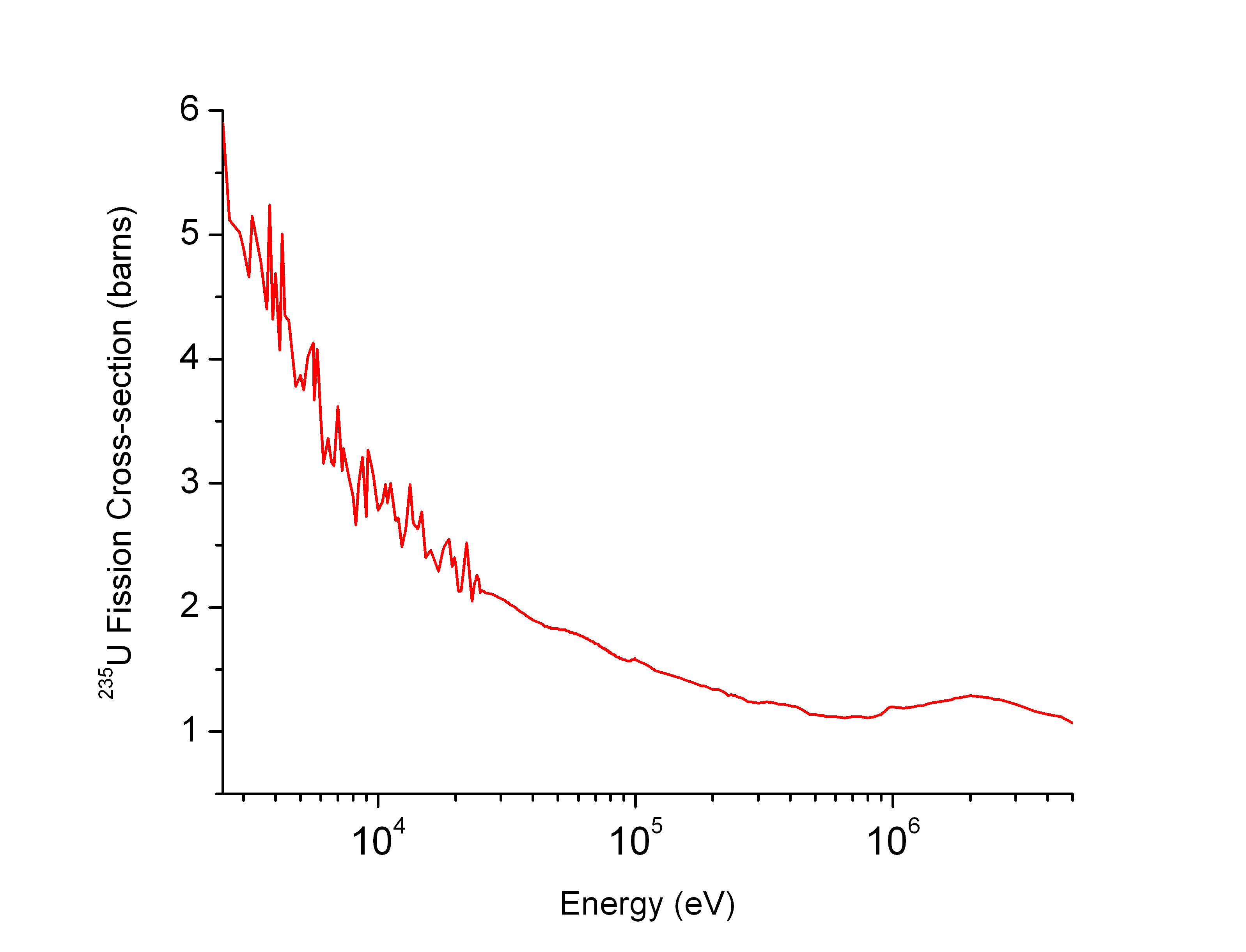
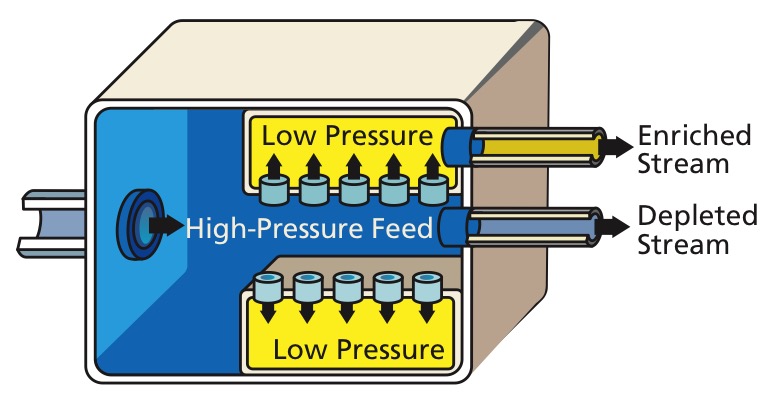
This isotope separation method was the first big successful method, having been used in the Manhattan Project, notably in the K-25 reactor.
This method was superseded by the more efficient gas centrifuges.
Comptes rendus de l'Académie des Sciences by  Ciro Santilli 40 Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
Ciro Santilli 40 Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
Apparently there were biweekly reports, that were grouped and published biannually on January and July, each one with a sequential tome number.
For example, both Marie Curie's Polonium paper and Marie Curie's Radium paper were published in the second half of 1898 and fell in tome 127.
Public domain publication list: archive.org/search?query=comptes+rendus+academie+des+sciences&sort=-date&and%5B%5D=collection%3A%22pub_comptes-rendus-hebdomadaires-academie-des-sciences%22 but some years are randomly missing like 1898?
OK from here you can find all of them more clearly: www.academie-sciences.fr/en/Transmettre-les-connaissances/comptes-rendus-de-l-academie-des-sciences-numerisees-sur-le-site-de-la-bibliotheque-nationale-de-france.html
The RaLa Experiment by Our Own Devices
. Source. Has some good mentions of Uranium vs Plutonium in nuclear weapon design.Bibliography:
- Open Q&As:
- Closed Q&As:
The Soviet Union's Deadly Abandoned Nuclear Generators by Andy Mcloone
. Source. - youtu.be/NT8-b5YEyjo?t=1435 epic orphan source recovery video
There are unlisted articles, also show them or only show them.