American plutonium production Created 2024-08-27 Updated 2025-07-16
sgp.fas.org/othergov/doe/pu50yc.html mentions:That site also contains a good summary of the closed shutdown reactors in each site. These are publicly disclosed e.g. at: www.hanford.gov/page.cfm/ProjectsFacilities
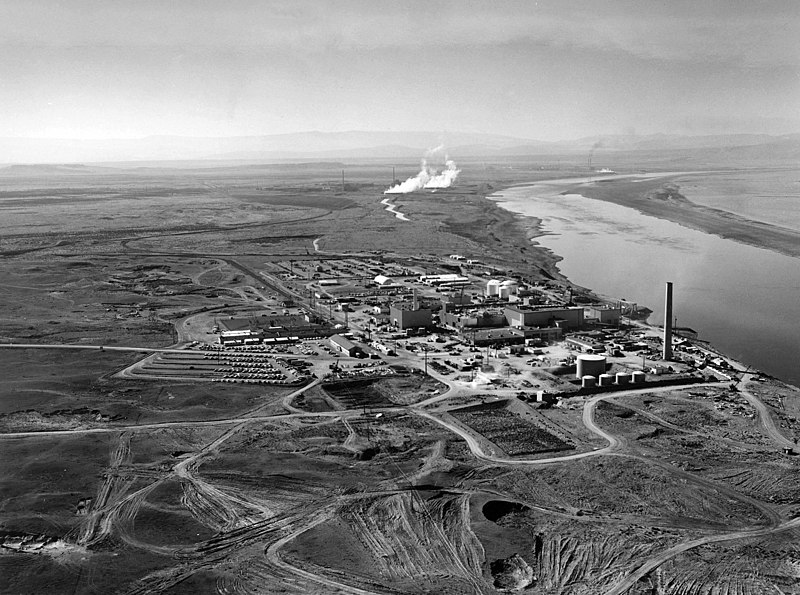
The United States Government has used 14 plutonium production reactors at the Hanford and Savannah River sites to produce plutonium for the U.S. nuclear weapons stockpile and DOE research and development programs. From 1944 to 1994, these reactors produced 103.4 metric tons of plutonium; 67.4 MT at Hanford, and 36.1 at Savannah River.
www.youtube.com/watch?v=qwKhz7BPBLY mentions that before they stopped production at the end of the Cold War, Hanford site produced 2/3 of the total American stockpile, and Savannah River site produced 1/3.
www.reuters.com/article/world/americas-nuclear-headache-old-plutonium-with-nowhere-to-go-idUSKBN1HR1JT/ claims that as of 2018 Savannah River site stored the majority of the stockpile.
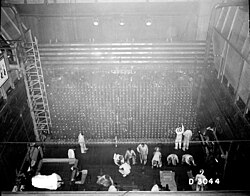
B Reactor Updated 2025-07-16
This was the first full scale nuclear reactor in the world, and was brought up slowly to test it out.
Hanford B Reactor tour by Studio McGraw
. Source. 2016.- youtu.be/8rlVHEY7BF0?t=335 good description of the fuel element. It uses uranium metal, not Uranium dioxide
- youtu.be/8rlVHEY7BF0?t=652 N Reactor and F Reactor were identical, and came up 2 months later, but much faster because of what they learned on the B
Fat Man Updated 2025-07-16
plutonium-based.
Its plutonium was produced at Hanford site.
Hanford site Updated 2025-07-16
The B Reactor of the facility produced the plutonium used for Trinity and Fat Man, and then for many more thousand bombs during the Cold War. More precisely, this was done at
Located in Washington, in a dry place the middle of the mountainous areas of the Western United States, where basically no one lives. The Columbia river is however nearby, that river is quite large, and provided the water needed by their activities, notably for cooling the nuclear reactors. It is worth it having look on Google Maps to get a feel for the region.
Unlike many other such laboratories, this one did not become a United States Department of Energy national laboratories. It was likely just too polluted.
Bibliography:
Nuclear reactor Updated 2025-07-16
Some of the most notable ones:
- 1942: Chicago Pile-1: the first human-made nuclear chain reaction.
- 1943: X-10 Graphite Reactor: an intermediate step between the nuclear chain reaction prototype Chicago Pile-1 and the full blown mass production at Hanford site. Located in the Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
- 1944: B Reactor at the Hanford site produced the plutonium used for Trinity and Fat Man
Savannah River site Created 2024-08-27 Updated 2025-07-16
This was one of the two American plutonium production sites, together with the Hanford site. www.youtube.com/watch?v=qwKhz7BPBLY mentions it produced about 1/3 of the total American plutonium.
www.reuters.com/article/world/americas-nuclear-headache-old-plutonium-with-nowhere-to-go-idUSKBN1HR1JT/ claims that as of 2018 it stored the majority of the plutonium stockpile of the country.
Trinity (nuclear test) Updated 2025-07-16
Plutonium-based.
Its plutonium was produced at Hanford site.
Trinity: Getting The Job Done
. Source. Good video, clarifies several interesting technical points:- Gun-type fission weapon were much easier to build as you don't need super synchronized charges as in implosion-type fission weapon. But they are less efficient.
- Plutonium make much more efficient usage of uranium, because you don't need to highly enrich a bunch of Uranium-235 in the first place, but rather just use way less enriched Uranium-235 to produce a bunch of Plutonium by converting Uranium-238
X-10 Graphite Reactor Updated 2025-07-16
This was an intermediate step between the nuclear chain reaction prototype Chicago Pile-1 and the full blown plutonium mass production at Hanford site. Located in the Oak Ridge National Laboratory.