Breeder reactor Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
A nuclear reactor made to produce specific isotopes rather than just consume fissile material to produce electrical power. The most notably application being to produce Plutonium-239 for nuclear weapons from Uranium-238 being irradiated from Uranium-235-created fission.
Gun-type fission weapon Updated 2025-07-16
Gun-type fission weapons are the simplest approach and they work with Uranium-235 bombs as you can ignite it with just one explosion.
But Gun-type fission weapons don't work with plutonium, and weapon grade Plutonium is cheaper than weapon grade Uranium, so it wasn't much used.
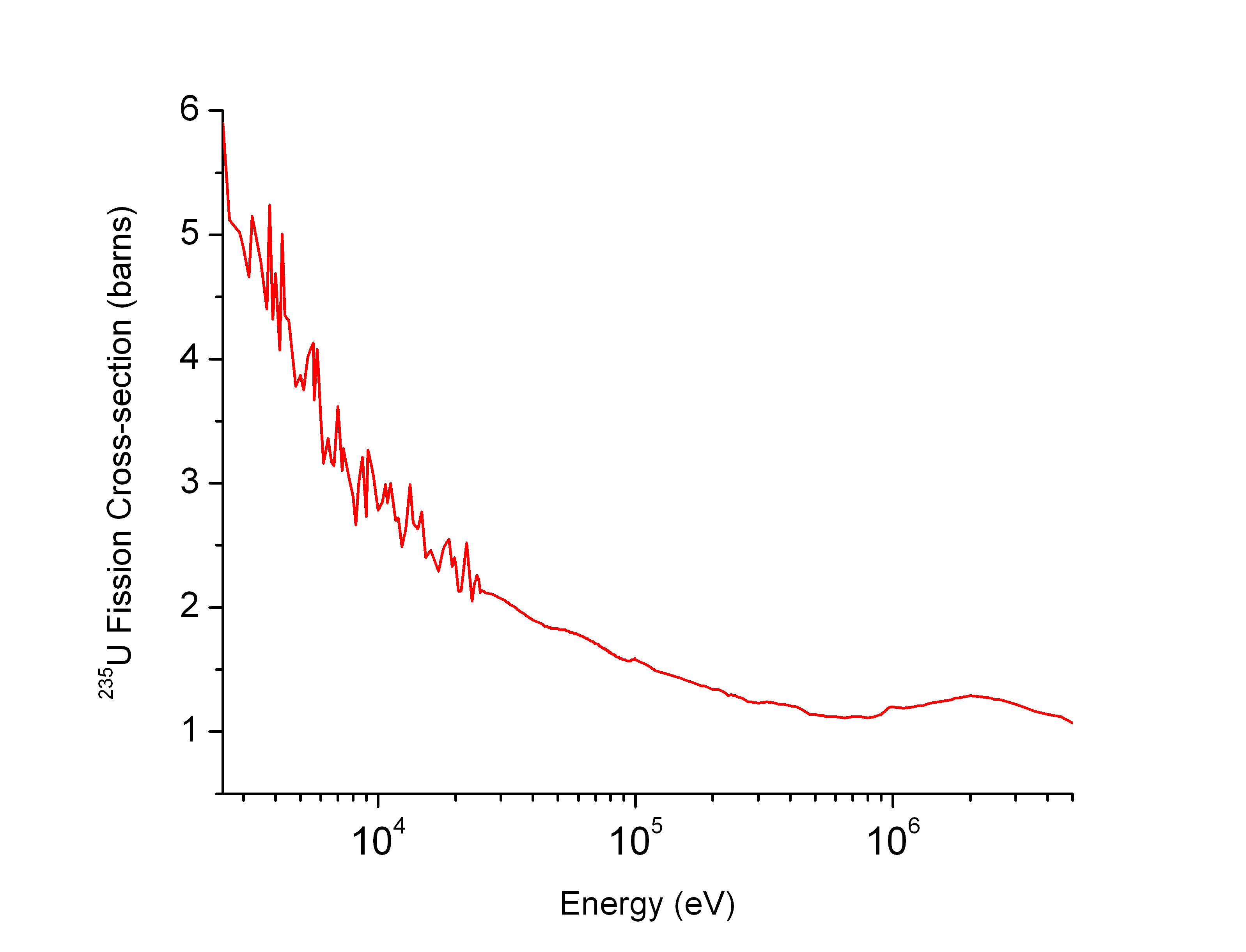
Neutron cross section Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
Oak Ridge National Laboratory Updated 2025-07-16
Located in Tennessee in the East of the United States.
The precursor organization to ORNL was called Clinton Engineer Works, where groundbreaking Manhattan Project experiments and nuclear production took place during World War II
Some key experiments carried out there include:
- 1943: X-10 Graphite Reactor: prototype Plutonium breeder reactor
- isotope separation to purify Uranium-235:
Trinity (nuclear test) Updated 2025-07-16
Plutonium-based.
Its plutonium was produced at Hanford site.
Trinity: Getting The Job Done
. Source. Good video, clarifies several interesting technical points:- Gun-type fission weapon were much easier to build as you don't need super synchronized charges as in implosion-type fission weapon. But they are less efficient.
- Plutonium make much more efficient usage of uranium, because you don't need to highly enrich a bunch of Uranium-235 in the first place, but rather just use way less enriched Uranium-235 to produce a bunch of Plutonium by converting Uranium-238
Weapons-grade nuclear material Created 2024-08-27 Updated 2025-07-16
For nuclear weapons you need a certain level of isotope purity of either plutonium-239 or uranium-235.
And the easiest way by far to achieve this purity is to produce plutonium-239 in a breeder reactor, which allows you to get it out with much cheaper chemical processes rather than costly isotope separation methods.