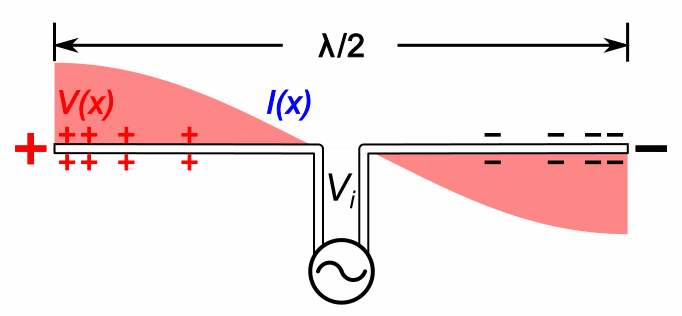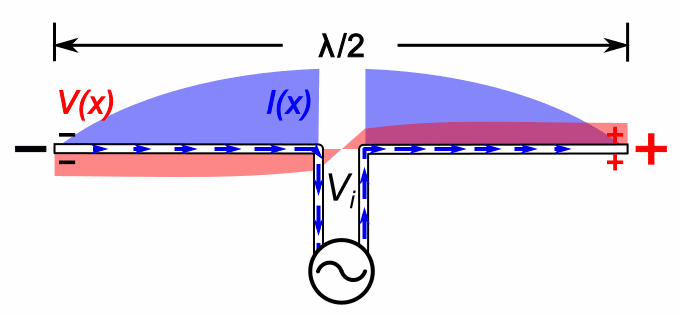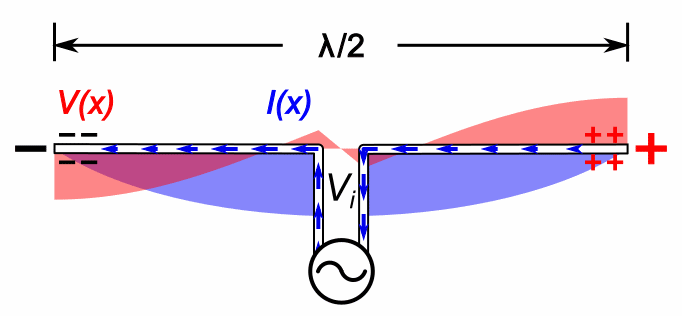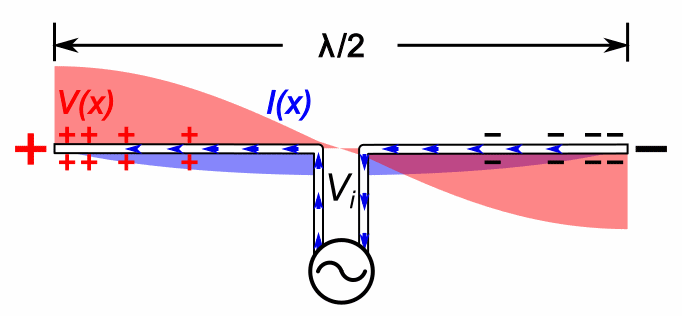
Heinrich Hertz's main initial experiment used a spark-gap transmitter. It is not something that transmits recorded sounds like voice: it only transmits noisy beeps. And as such was used for wireless telegraphy.
- a piezo igniter from a barbequeue lighter
- a more powerful home-made transformer
Hertz and Radio waves Explained by PhysicsHigh (2016)
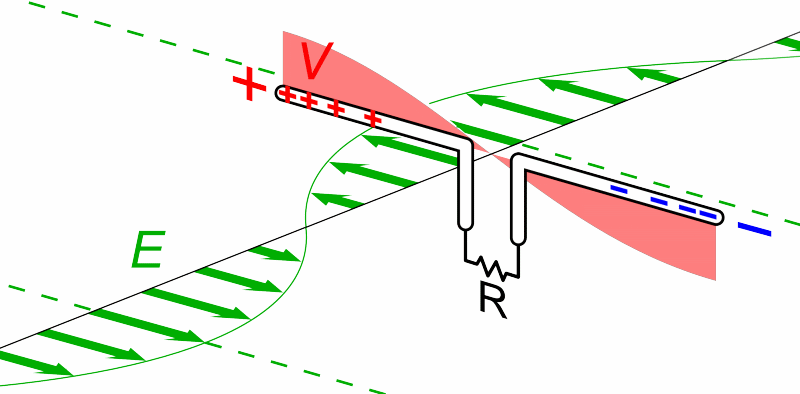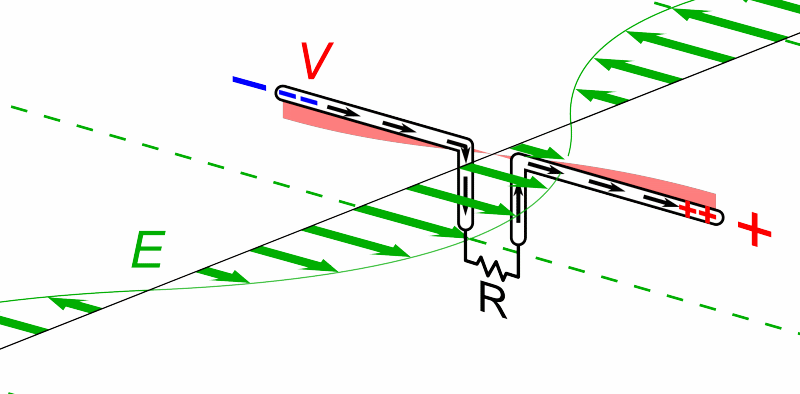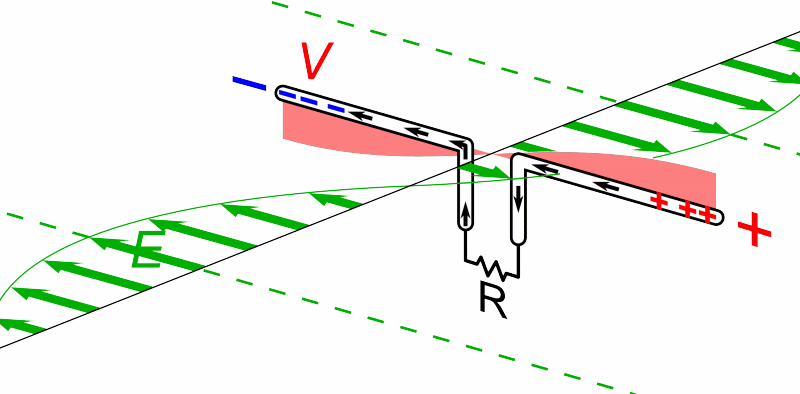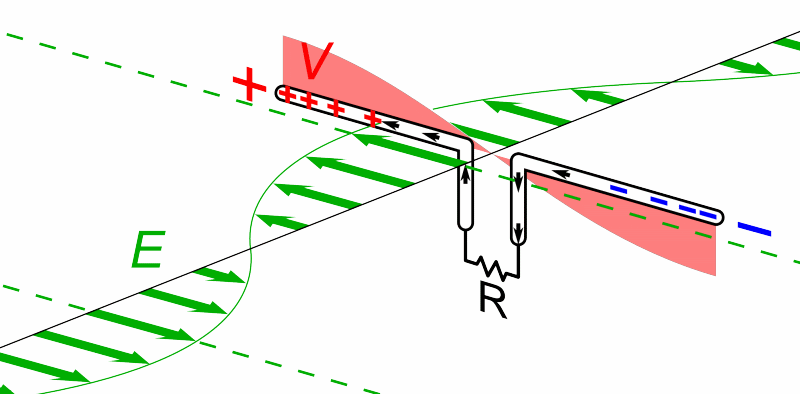
Source. Simple schematics showing the basics of the experiments. No choice of components rationale.But now people want to send voice. How to do it?
It would not be practical without modulation: Why can't you send voice without modulation?
Basically, the antenna has to be very, very large, more comparable to wavelength. E.g. even for the higher pitches, we fall in very low frequency, so have a look at the size of some of the submarine VLF antennas! They are like football pitch sized.
To send voice and music, amplitude modulation had to be developed. And a key ingredient of this is the carrier wave.
The problem is, the carrier wave needs to have somewhat high frequencies, in the hundreds of kHz TODO why. But as you might imagine, that is hard to achieve by mechanical means such as a hand cranck like Hippolyte Pixiis alternator!
Interestingly, some of the first carrier wave generators were actually mechanical, e.g. the Alexanderson alternator.
But clearly such mechanical machines were not very scalable, and soon more electronic devices were introduced, notably the vacuum tube.
Radio Wave Properties: Electric and Magnetic Dipole Antennae by Harvard Natural Sciences Lecture Demonstrations (2020)
Source. The dude lights bulbs on an antenna made of a single piece of copper, powered with EM radiation. Amazing.As well put by Wikipedia, a radio receiver has to perform three functions on the signal from the antenna:
- filtering, so you can tune the station you care about. This filters based on the frequency of the carrier wave you want. I.e. you use a bandpass filter.
- amplification: otherwise you won't be able to hear anything if the emitter is too far away
- demodulation: this means decoding the signal based on whatever way it was encoded, notably e.g. AM/FM
The first type of device that allowed sending Morse code without wires, as opposed to the wired electrical telegraph that previously existed.
Wireless voice transmission came about with modulation.
Articles by others on the same topic
Radio is a technology that uses radio waves to transmit and receive information, typically audio content. It operates by encoding sound into electromagnetic waves, which can travel through the air over varying distances. Here's a breakdown of its key components and functions: 1. **Transmission**: Radio transmitters convert audio signals into radio waves and broadcast them through an antenna. These signals can be amplitude modulated (AM) or frequency modulated (FM), allowing for different qualities of sound and range.