As mentioned at: math.stackexchange.com/questions/579453/real-world-application-of-fourier-series/3729366#3729366 from solving partial differential equations with the Fourier series citing courses.maths.ox.ac.uk/node/view_material/1720, analogously to the heat equation, the wave linear equation can be be solved nicely with separation of variables.
Staring from a triangle wave, this explains why we always get the same musical notes:See also: solving partial differential equations with the Fourier series.
- www.math.hmc.edu/~ajb/PCMI/lecture7.pdf "7.5.1. Musical instruments" is very good. Also mentions that in the piano it is more like an initial speed is applied, and it is not the same as plucking
- music.stackexchange.com/questions/135635/confusion-about-overtones-and-a-slow-motion-video-of-a-plucked-string
- music.stackexchange.com/questions/60833/what-determines-the-relative-volumes-of-the-harmonics-when-plucking-a-guitar-str
This section talks about solvers/simulators dedicated solving the wave equation. Of course, any serious solver will likely be able to solve a wider range of PDE, so this section contains mostly fun toys. For more serious stuff see: Section "PDE solver".
JavaScript toy solvers:
- jtiscione.github.io/webassembly-wave/index.html circular domain, create waves with mouse click
- dionyziz.com/graphics/wave-experiment/ with useless 3D WebGL visualization :-), waves with mouse click. Solving itself done on CPU, not GPU.
web.archive.org/web/20200621205928/https://courses.maths.ox.ac.uk/node/view_material/1720 also mentioned at math.stackexchange.com/questions/579453/real-world-application-of-fourier-series/3729366#3729366 from heat equation solution with Fourier series.
TODO confirm, see also: coupled oscillators. And then this idea can be used to define/motivate quantum field theory in terms of quantum harmonic oscillators with second quantization.
- youtu.be/SMmFgIEGYtw?t=324 Quantum Field Theory 2a - Field Quantization I by ViaScience (2018)
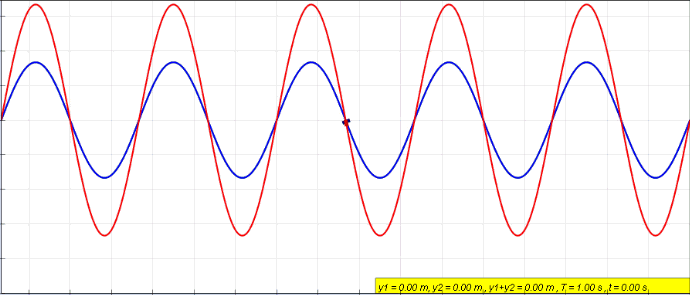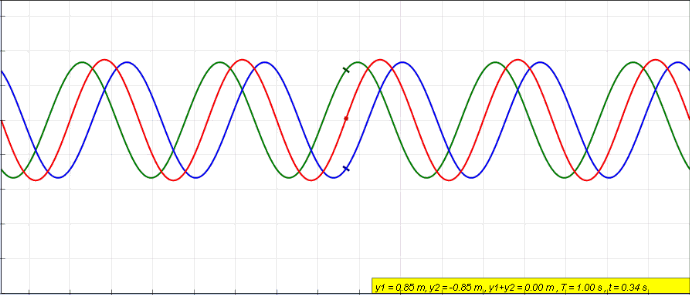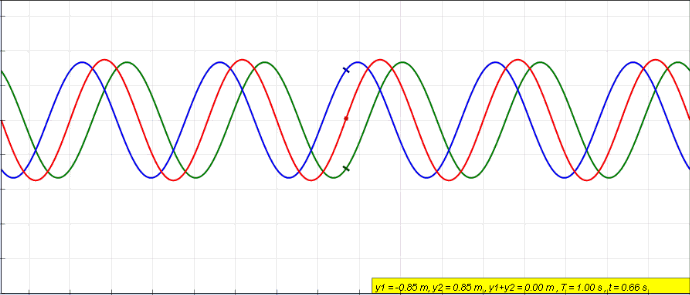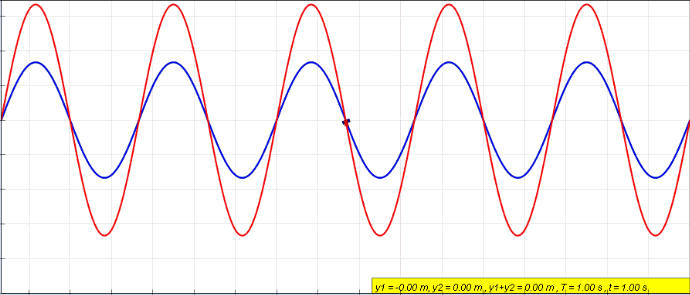
Standing wave caused by wave interference of two waves
. Source. Start with: Section "String polarization".
Then go to: Section "Polarization of light".
This is about the polarization of a string in 3D space. That is the first concept of polarization you must have in mind!
Far field approximation to Kirchhoff's diffraction formula, i.e. when the plane of observation is far from the object diffracting.
Near field approximation to Kirchhoff's diffraction formula, i.e. when the plane of observation is near the object diffracting.
Examples:
- mechanical resonance, notably:
- pipe instruments
- electronic oscillators, notably:
- LC oscillator, and notably the lossy version RLC circuit
Perhaps a key insight of resonance is that the reonant any lossy system tends to look like the resonance frequency quite quickly even if the initial condition is not the resonant condition itself, because everything that is not the resonant frequency interferes destructively and becomes noise. Some examples of that:
- striking a bell or drum can be modelled by applying an impuse to the system
- playing a pipe instrument comes down to blowing a piece that vibrates randomly, and then leads the pipe to vibrate mostly in the resonant frequency. Likely the same applies to bowed string instruments, the bow must be creating a random vibration.
- playing a plucked string instrument comes down to initializing the system to an triangular wave form and then letting it evolve. TODO find a simulation of that!
Another cool aspect of resonance is that it was kind of the motivation for de Broglie hypothesis, as de Broglie was kind of thinking that electroncs might show discrete jumps on atomic spectra because of constructive interference.
Notably used for the pattern of the double-slit experiment.
Shows up when trying to solve 2D wave equation on a circular domain in polar coordinates with separation of variables, where we have to decompose the initial condition in termes of a fourier-Bessel series, exactly like the Fourier series appears when solving the wave equation in linear coordinates.
For the same fundamental reasons, also appears when calculating the Schrödinger equation solution for the hydrogen atom.
Completeness: math.stackexchange.com/questions/2192665/is-this-set-of-bessel-functions-a-basis-for-all-c10-a-functions TODO
This is the Bessel function analogue to Fourier basis is complete for .
eigenvalue problem of Laplace's equation.