Ainan Celeste Cawley Updated 2025-07-16
His father fought a lot with the stupid educational system to try and move his son to his full potential and move to more advanced subjects early.
A crime of society to try and prevent it. They actually moved the family from Singapore to Malaysia for a learning opportunity for the son. Amazing.
This is the perfect illustration of one of Ciro Santilli's most important complaints about the 2020 educational system:and why Ciro created OurBigBook.com to try and help fix the issue.
Bibliography:
Ainan Cawley: Child prodigy (2013)
Source. - youtu.be/Ugi74cwPMSg?t=137 finding the right school
Cherwell (newspaper) Updated 2025-07-16
Crankstart Foundation Updated 2025-07-16
At crankstart.org/grants the organization's website describes mostly California activities, but they do at least also act in the University of Oxford, see: Section "University of Oxford study costs".
Presumably the name refers to crank starting an old car, as in helping out those in difficulty like poor students get started in life. But is also an obscure slang for a type of handjob according to Urban Dictionary.
Kleiner Perkins Updated 2025-07-16
John Doerr Q&A at Berkeley (2015)
Source. - youtu.be/4xWGSUZmkIc?t=634 invest in batteries
Korean drama Updated 2025-07-16
www.nytimes.com/2023/07/09/world/asia/north-korea-china-defectors.htmlK-drama, the ultimate symbol of resistance. Epic.
North Korea keeps itself cut off from the internet and sends these highly trained specialists to do work in China, Southeast Asia and elsewhere to avoid international sanctions imposed on the country for its nuclear weapons program. The specialists usually live together in dormitory apartments, where they are instructed to spy on each other. Their North Korean minders look for signs of disloyalty - like watching K-dramas.
UK cycle route Updated 2025-07-16
Mexican drug war Updated 2025-07-16
Place de la République Updated 2025-07-16
Raga Updated 2025-07-16
Compton scattering Updated 2025-07-16
Classic theory predicts that the output frequency must be the same as the input one since the electromagnetic wave makes the electron vibrate with same frequency as itself, which then irradiates further waves.
But the output waves are longer because photons are discrete and energy is proportional to frequency:
The formula is exactly that of two relativistic billiard balls colliding.
Compton Scattering by Compton Scattering (2017)
Source. Experiment with a caesium-137 source.L3.3 Compton Scattering by Barton Zwiebach (2017)
Source. C++ Updated 2025-07-16
C plus plus is what you get when you want to have all of:
Superconducting temperature Updated 2025-07-16
Tetrapod Updated 2025-07-16
Includes:
- amphibians
- amniotes, which includes:
- sauropsida: reptiles and birds, which really are reptiles
- mammals
The exact relationships between those clades is not very clear as there's a bunch of extinct species in the middle we are not sure exactly where they go exactly, some hypothesis are listed at: en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Tetrapod&oldid=1053601110#Temnospondyl_hypothesis_(TH)
Voltmeter Updated 2025-07-16
AI training robot Updated 2025-07-16
It doesn't need to be a bipedal robot. We can let Boston Dynamics worry about that walking balance crap.
It could very well instead be on wheels like arm on tracks.
Or something more like a factory with arms on rails as per:
- Transcendence (2014)
- youtu.be/MtVvzJIhTmc?t=112 from Video "Rotrics DexArm is available NOW! by Rotrics (2020)" where they have a sliding rail
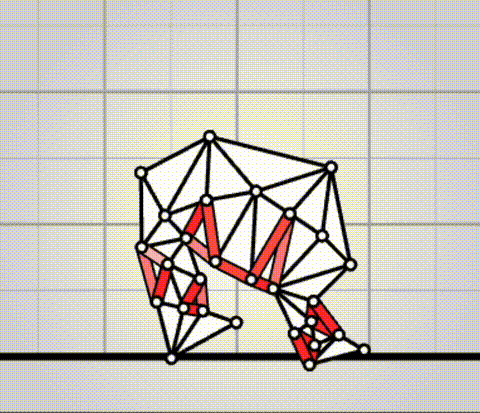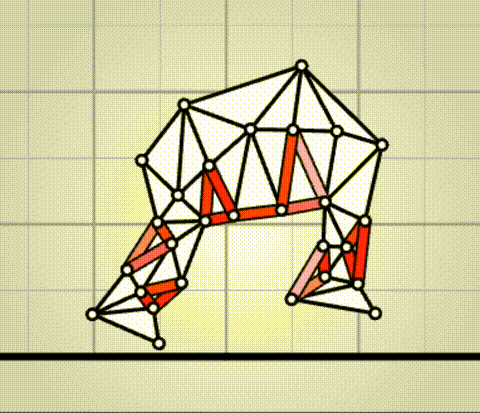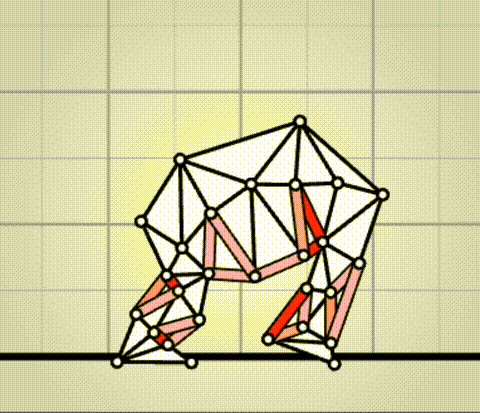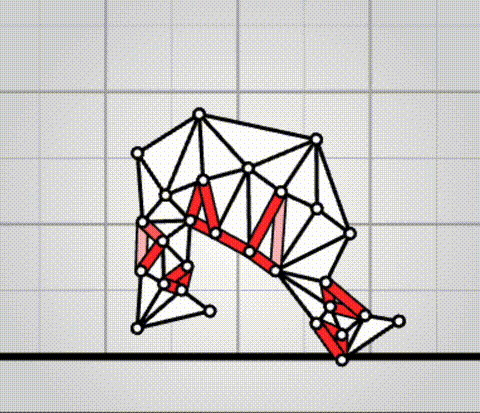
Algovivo demo
. github.com/juniorrojas/algovivo: A JavaScript + WebAssembly implementation of an energy-based formulation for soft-bodied virtual creatures. Alain Aspect Updated 2025-07-16
Diffraction of light Updated 2025-07-16
Zettelkasten Updated 2025-07-16
zettelkasten.de/posts/overview/ mentions one page to rule them all:
How many Zettelkästen should I have? The answer is, most likely, only one for the duration of your life. But there are exceptions to this rule.
Alan Watts controlled dream of life talk Updated 2025-07-16
Goes along: if you could control your life multiple times to be perfect, you would eventually get tired of paradise, and you would go further and further into creating uncertain worlds with some suffering, until you would reach the current real world.
Very similar to The Matrix (1999) when Agent Smith talks about the failed Paradise Matrix shown at www.youtube.com/watch?v=9Qs3GlNZMhY:
Did you know that the first Matrix was designed to be a perfect human world where none suffered, where everyone would be happy? It was a disaster. No one would accept the program. Entire crops were lost. Some believed that we lacked the programming language to describe your "perfect world". But I believe that, as a species, human beings define their reality through misery and suffering. So the perfect world was a dream that your primitive cerebrum kept trying to wake up from.
Albuquerque, New Mexico Updated 2025-07-16
There are unlisted articles, also show them or only show them.