Maxwell Lagrangian Updated 2025-07-16
- www.youtube.com/watch?v=nrBiDRZRK5g Maxwell Lagrangian Derivation by Dietterich Labs (2019)
- www.youtube.com/watch?v=yo-Z3RO-eeY Deriving the Maxwell Lagrangian by Pretty Much Physics (2019)
Reverse debugging Updated 2025-07-16
Why it takes several days to enter inflammatory phase in COVID-19? Updated 2025-07-16
Why is it there such a clear separation of phases?
Why do people with mild symptoms go on to die? It is a great mystery.
Ciro Santilli's theory is that COVID is extremely effective at avoiding immune response. Then, in people where this is effective, things reach a point where there is so much virus, that the body notices and moves on to take a more drastic approach. This is compatible with the virus killing older people more, as they have weaker immunes systems. This is however incompatible with the fact that people don't seem to be contagious after the viral phase is over...
Xerox PARC Updated 2025-07-16
What a legendary place.
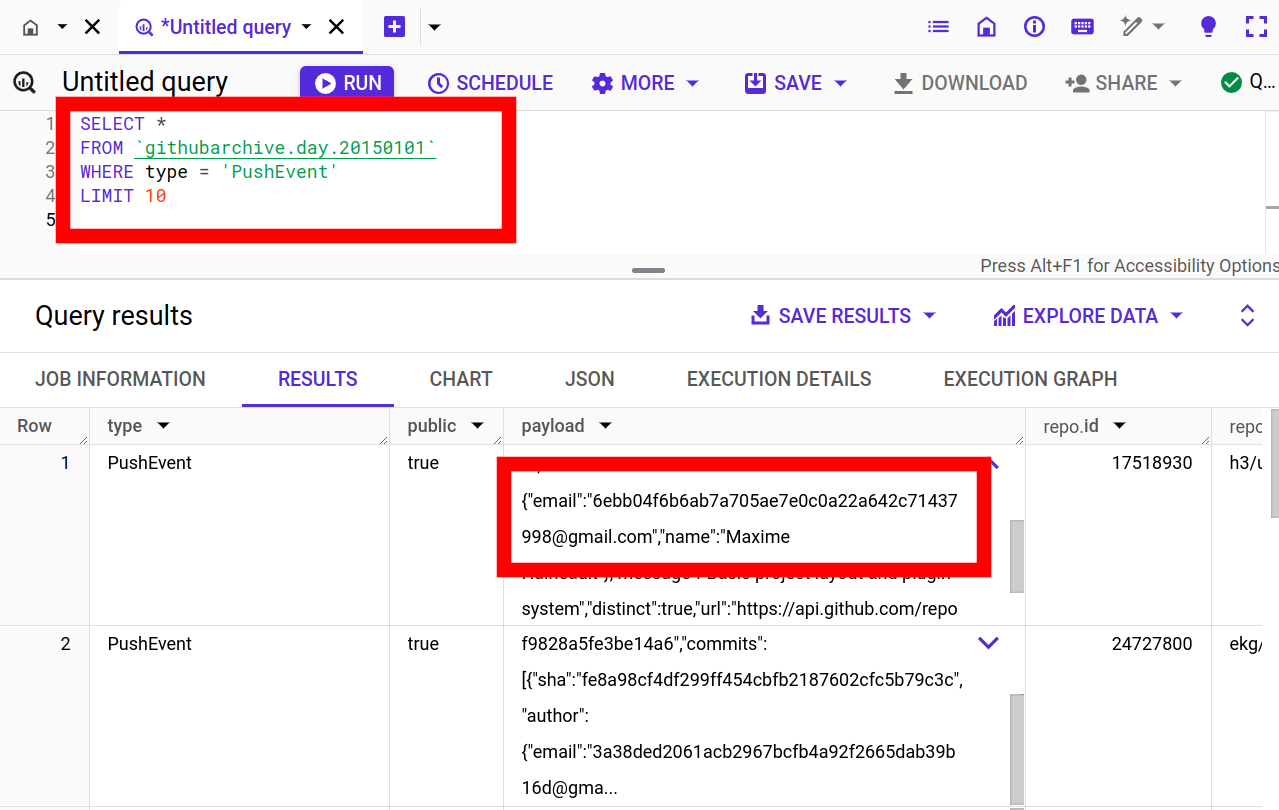
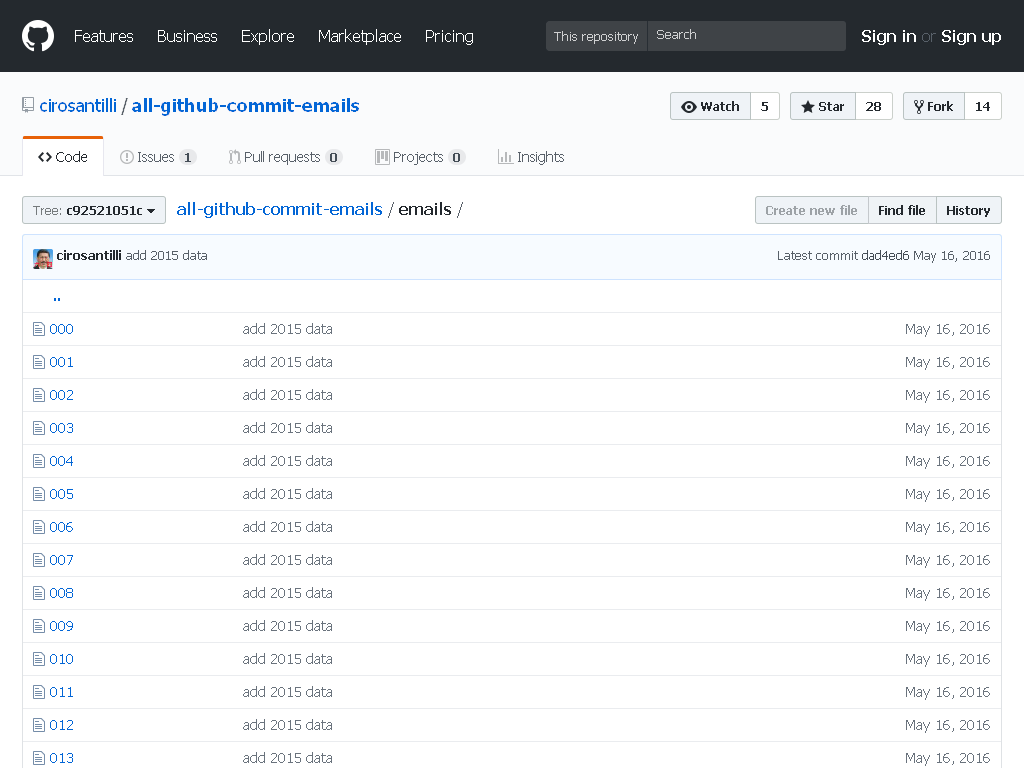
All GitHub Commit Emails Updated 2025-07-16
In this project Ciro Santilli extracted (almost) all Git commit emails from GitHub with Google BigQuery! The repo was later taken down by GitHub. Newbs, censoring publicly available data!
Ciro also created a beautifully named variant with one email per commit: github.com/cirosantilli/imagine-all-the-people. True art. It also had the effect of breaking this "what's my first commit tracker": twitter.com/NachoSoto/status/1761873362706698469
GitHub Archive query showing hashed emails
. It was Ciro Santilli that made them hash the emails. They weren't hashed before he published the emails publicly.All GitHub Commit Emails repo before takedown
. Screenshot from archive.is. All indefinite orthogonal groups of matrices of equal metric signature are isomorphic Updated 2025-07-16
Following the definition of the indefinite orthogonal group, we want to show that only the metric signature matters.
First we can observe that the exact matrices are different. For example, taking the standard matrix of :and:both have the same metric signature. However, we notice that a rotation of 90 degrees, which preserves the first form, does not preserve the second one! E.g. consider the vector , then . But after a rotation of 90 degrees, it becomes , and now ! Therefore, we have to search for an isomorphism between the two sets of matrices.
For example, consider the orthogonal group, which can be defined as shown at the orthogonal group is the group of all matrices that preserve the dot product can be defined as:
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors Updated 2025-07-16
Eigenvectors and eigenvalues of the identity matrix Updated 2025-07-16
Ł Updated 2025-07-16
Television series that Ciro Santilli watched all episodes of Updated 2025-07-16
Ten ancient famous songs of China Updated 2025-07-16
Brexit Updated 2025-07-16
British politician Updated 2025-07-16
Eight Chinese Cuisines Updated 2025-07-16
This classification is too restrictive, and too South-centered. But if is worth knowing.
Electron crystallography Updated 2025-07-16
Crystallography determination with a transmission electron microscopy instead of the more classical X-ray crystallography.
Zebrafish Updated 2025-07-16
BIOS Updated 2025-07-16
Compiled programming language Updated 2025-07-16
Dan Kaminsky approves Linux Kernel Module Cheat Updated 2025-07-16
E. Coli origin of replication Updated 2025-07-16
There are unlisted articles, also show them or only show them.