On a new, strongly radioactive substance contained in pitchblende Created 2024-08-15 Updated 2025-07-16
This is the paper where Marie Curie announced the discovery of Radium.
It came out only 6 months after the Polonium paper and ended up in the same tome of the Comptes rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, number 127 which is funny.
French text on Wikisource: fr.wikisource.org/wiki/Œuvres_de_Pierre_Curie/24. It's from a 1908 collection of works, and it has made minor corretions, such as using "radioactive" without dash instead of "radio-active" to update the terminology a bit, which is a crime!
The original can be found inside the original tome PDF: archive.org/details/ComptesRendusAcademieDesSciences0127/page/n5/mode/2up
An English translation by the American Institute of Physics: history.aip.org/exhibits/curie/discover.htm
Basically they extracted a Barium solution, but were unable to separate Barium and Radium. If you look at a periodic table, you will see that Radium is directly below radium which explains it as they have very similar chemical properties.
Two of us have shown that by purely chemical procedures it is possible to extract from pitchblende a strongly radio-active substance. This substance is related to bismuth by its analytical properties. We have expressed the opinion that perhaps the pitchblende contained a new element, for which we have proposed the name of polonium.The investigations which we are following at present are in agreement with the first results we obtained, but in the course of these investigations we have come upon a second, strongly radio-active substance, entirely different from the first in its chemical properties. Specifically, polonium is precipitated from acid solution by hydrogen sulfide; its salts are soluble in acids and water precipitates them from solution; polonium is completely precipitated by ammonia.The new radio-active substance which we have just found has all the chemical appearance of nearly pure barium: it is not precipitated either by hydrogen sulfide or by ammonium sulfide, nor by ammonia; its sulfate is insoluble in water and in acids; its carbonate is insoluble in water; its chloride, very soluble in water, is insoluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid and in alcohol. Finally this substance gives the easily recognized spectrum of barium.
Like with Polonium they once again found a new spectral line, though it was somewhat weak in this case as they didn't manage to purify as much:
M. Demarçay has consented to examine the spectrum of our substance with a kindness which we cannot acknowledge too much. The results of his examinations are given in a special Note at the end of ours. Demarçay has found one line in the spectrum which does not seem due to any known element. This line, hardly visible with the chloride 60 times more active than uranium, has become prominent with the chloride enriched by fractionation to an activity 900 times that of uranium. The intensity of this line increases, then, at the same time as the radio-activity; that, we think, is a very serious reason for attributing it to the radio-active part of our substance.
Name the thing:
They did not have enough purity to clearly measure the mass difference:but it is cute to see that they called radium as "active barium".
We have measured the atomic weight of our active barium, determining the chlorine in its anhydrous chloride. We have found numbers which differ very little from those obtained in parallel measurements on inactive barium chloride; the numbers for the active barium are always a little larger, but the difference is of the order of magnitude of the experimental errors.
Polonium and radium can be used as a light source without power source, so oops, it looks like we broke the conservation of energy!Later on radium came to be used as a phosphorescent light source for things like watch handles, which led to girls getting cancer in the factories; the Radium Girls.
The new radio-active substance certainly includes a very large portion of barium; in spite of that, the radio-activity is considerable. The radio-activity of radium then must be enormous.Uranium, thorium, polonium, radium, and their compounds make the air a conductor of electricity and act photographically on sensitive plates. In these respects, polonium and radium are considerably more active than uranium and thorium. On photographic plates one obtains good impressions with radium and polonium in a half-minute's exposure; several hours are needed to obtain the same result with uranium and thorium.The rays emitted by the components of polonium and radium make barium platinocyanide fluorescent; their action in this regard is analogous to that of the Röntgen rays, but considerably weaker. To perform the experiment, one lays over the active substance a very thin aluminum foil on which is spread a thin layer of barium platinocyanide; in the darkness the platinocyanide appears faintly luminous above the active substance.
On a new radioactive substance contained in pitchblende Created 2024-08-15 Updated 2025-07-16
This is the papaer where Marie Curie announced the discovery of Polonium.
Here's a link with OCR on the French Wikisource: fr.wikisource.org/wiki/%C5%92uvres_de_Pierre_Curie/23. It's from a 1908 collection of works, but it is the exact same paper.
First a recap of previous work:Note the cute terminology "Becquerel rays", which were only later understood to be electromagnetic radiation now known as gamma rays.
Some minerals containing uranium and thorium (pitchblende, chalcolite, uranite) are very active from the point of view of the emission of Becquerel rays. In a previous work, one of us showed that their activity is even greater than that of uranium and thorium, and expressed the opinion that this effect was due to some other very active substance contained in small quantities in these minerals.
Then some more recapitulation of the previously discussed groundbreaking idea that only atom counts matter for radioactivity, regardless of their chemical configuration as in fluorescence:
The study of compounds of uranium and thorium had shown, in fact, that the property of emitting rays which make air conductive and which act on photographic plates is a specific property of uranium and thorium which is found in all compounds of these metals, all the more weakened as the proportion of active metal in the compound is itself lower. The physical state of the substances seems to have a completely secondary importance. Various experiments have shown that the state of mixture of the substances seems to act only by varying the proportion of active bodies and the absorption produced by the inert substances. Certain causes (such as the presence of impurities) which act so powerfully on phosphorescence or fluorescence are therefore here completely without action. It therefore becomes very probable that if certain minerals are more active than uranium and thorium, it is because they contain a substance more active than these metals.
Then the key innovation: they used radioactivity measures to guide their purification work:
We have sought to isolate this substance in pitchblende, and experience has confirmed the above predictions.Our chemical research has been constantly guided by the control of the radiant activity of the products separated at each operation. Each product is placed on one of the plates of a condenser, and the conductivity acquired by the air is measured using an electrometer and a piezoelectric quartz, as in the work cited above. We thus have not only an indication but a number which accounts for the richness of the product in active substance.
Next they describe in high level their separation process, and I can't understand anything. But that's OK
Finally towards the end, bombs are dropped:
- the new elemnt is next to bismuth. If you stop now and look at a periodic table, you will see that bismuth is exactly one element before polonium
- "simple bodies" is their cute terminology for atoms, whose existence at the time not yet full aknowledged Section "History of the atomic theory"
- we call it polonium
By carrying out these various operations, we obtain increasingly active products. Finally, we obtained a substance whose activity is about 400 times greater than that of uranium.We have sought, among the bodies currently known, to see if there are any active ones. We have examined compounds of almost all simple bodies; thanks to the great kindness of several chemists, we have had samples of the rarest substances. Uranium and thorium are the only ones clearly active, tantalum is perhaps very weakly so.
They managed to purify it enough to look at the emission spectrum and it seems novel:
Mr. Demarçay was kind enough to examine the spectrum of the body that we are studying. He was unable to distinguish any characteristic line apart from those due to impurities. This fact does not support the idea of the existence of a new metal. However, Mr. Demarçay pointed out to us that uranium, thorium and tantalum offer particular spectra, formed of innumerable lines, very fine, difficult to perceive.
And once again, our radiation-based analytical chemistry technique is new:
Allow us to note that if the existence of a new element is confirmed, this discovery will be uniquely attributable to the new method of detection that Becquerel rays provide.
Updates
facial_recognition Python package Created 2024-08-15 Updated 2025-07-16superuser.com/questions/420885/is-there-a-face-recognition-command-line-tool/1852394#1852394 played with the
face_recognition Python package: github.com/ageitgey/face_recognition Cute CLI API, but disappointing accuracy. Also at:Thanks Adam Geitgey for putting that repo up.
Updates Marie Curie papers Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
Under Section "Publication by Marie Curie" I did a quick overview of the papers in which Marie Curie and collaborators publish the existence of new elements polonium and radium. Both are very understandable (except the chemistry), and have some cute terminology. I also cited those papers on her Wikipedia page: en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Marie_Curie&diff=1240252528&oldid=1238097626 Another good exercise in "old paper finding" + "Wikipedia markup/rules" as I looked at the Comptes rendus de l'Académie des Sciences a bit.
The RaLa Experiment by Our Own Devices
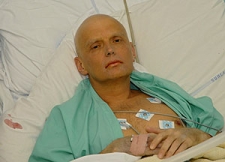
. Source. The poisoning of Alexander Litvinenko Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
Alexander Litvinenko Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
Russian dissident Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
Do all gamma rays have the same energy during a given nuclear reaction? Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
The following cobalt-60 diagrams suggest that some lines are clearly visible in specific nuclear reactions:
Also this one:
Alpha particles have low penetration depth Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
They are stopped by:Therefore, alpha emitters are not too dangerous unless ingested.
Comptes rendus de l'Académie des Sciences Tome 127 Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
This one contains a PDF with OCR: archive.org/details/ComptesRendusAcademieDesSciences0127/page/n5/mode/2up
Gun-type fission weapons don't work with plutonium Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
Gun-type fission weapons don't work with Plutonium-239 because of the presence of Plutonium-240 as an impurity which leads to fizzle.
Good mentions at: youtu.be/dgBDvnqMkT4?t=252
Gamma spectroscopy Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
Gamma spectroscopy of a Uranium ore
. Source. Several points of the Uranium 238 decay chain are clearly visible. Thorium-232 decay chain Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
Breeder reactor Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
A nuclear reactor made to produce specific isotopes rather than just consume fissile material to produce electrical power. The most notably application being to produce Plutonium-239 for nuclear weapons from Uranium-238 being irradiated from Uranium-235-created fission.
Tome of the Comptes rendus de l'Académie des Sciences Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
Weapon grade Plutonium is cheaper than weapon grade Uranium Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
Because you can generate plutonium-239 from uranium-238 in a breeder reactor, and then separate the plutonium-239 from the Uranium simply by using chemistry methods because you've created an element with different valence electrons.
Isn't it somewhat funny that it is easier to purify a synthetic element than a naturally occurring one?
Thorium-232 Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
GPHS-RTG Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
Polonium-209 Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
Polonium-208 Created 2024-08-14 Updated 2025-07-16
There are unlisted articles, also show them or only show them.