Platform as a service Updated 2025-07-16
Central processing unit Updated 2025-07-16
Country in South America Updated 2025-07-16
Jean Baptiste Perrin Updated 2025-07-16
Lattice gauge theory Updated 2025-07-16
River in South America Updated 2025-07-16
Country in South Asia Updated 2025-07-16
Jitsi Updated 2025-07-16
No chat only? .... community.jitsi.org/t/chat-function-only/79067
Appears to be based on XMPP: community.jitsi.org/t/jitsi-users-is-jitsi-a-regular-xmpp-server/13211
John the Baptist Updated 2025-07-16
Joint European Torus Updated 2025-07-16
Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia) Updated 2025-07-16
Josephson phase Updated 2025-07-16
It represents an internal state of the junction.
JSON Updated 2025-07-16
Legendre polynomials Updated 2025-07-16
Show up when solving the Laplace's equation on spherical coordinates by separation of variables, which leads to the differential equation shown at: en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Legendre_polynomials&oldid=1018881414#Definition_via_differential_equation.
Unitary group of degree 2 Updated 2025-07-16
Diffeomorphic to the 3 sphere.
Complementarity (physics) Updated 2025-07-16
Country in Southeast Asia Updated 2025-07-16
Energy operator Updated 2025-07-16
Appears directly on Schrödinger equation! And in particular in the time-independent Schrödinger equation.
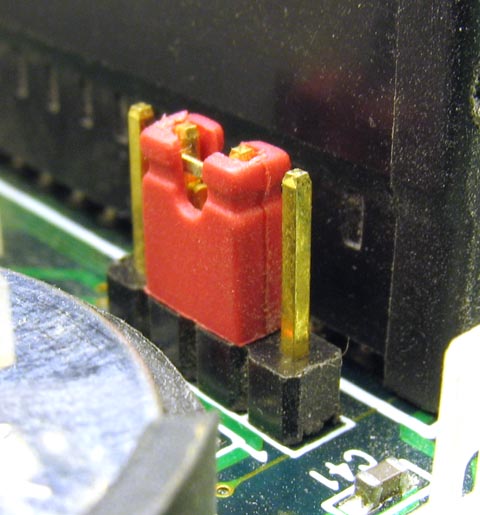
Jumper (computing) Updated 2025-07-16
K-12 Updated 2025-07-16
There are unlisted articles, also show them or only show them.