Messaging software that force you to share your mobile phone with contacts Updated 2025-07-16
Nerds 2.0.1 Updated 2025-07-16
Very very good. Those nice pre-Dot-com bubble vibes.
Might be freely watchable? Wikipedia links to:
But they do start with an FBI warning about copyright. So... erm.
Part 1 - Networking The Nerds talks about the TCP/IP and early machines implementing it:
- 21:00: shows inside The Pentagon. The way the dude who works there opens a his locked office door with an electric switch is just amazing. Cringely also mentions that there's an actual official speed limit in the corridors as he rides a carrier bike slowly through them.
- 21:45: the universities weren't enthusiastic, because people from other locations would be able to use your precious computer time. But finally ARPA forced the universities' hands, and they joined.
- 24:24 mentions that some of the guys who created ARPANET were actually previously counting cards at Casinos in Las Vegas, just like in the 21 (2008) film
- one of the centerpieces of development was at UCLA. The other was the BBN company. 33:55 shows the first router, then called them Interface Message Processor
- the first message was from UCLA to Stanford University. He was trying to write "Login", and it crashed at the 'g'. Epic. They later debugged it.
- towards the end talks about ALOHAnet, the first wireless computer communication done
Part 2 - Serving the Suits
- Robert Metcalfe. He's nice. Xerox PARC. Ethernet.
- Explains what is a "Workstation", notably showing one by Sun Microsystems. This is now an obscure "passé" thing in 2020 that young people like Ciro Santilli have only heard of in legend (or in outdated university computer labs!). Funny to think that so many people have had this idea before, including e.g. the Chromebook
- 10:46 mentions that all of Cisco, Silicon Graphics and Sun Microsystems and where founded at Margaret Jacks Hall, Building 460, at Stanford University.
- he then talks a lot about Sun. Sun became dominant in Wall Street.
- 19:05: Novell, from Utah. How they almost went bust, but were saved at the last moment by Ray Noorda, who refocused them to their NetWare product which was under recent development. It allowed file and printer sharing in IBM PCs. 22:55 shows how they had a live radio host for people waiting on customer support calls!
- 33:56 mentions how The Grateful Dead had in impact on the Internet, as people wanted computers to be able to access The WELL online forum. They still own the domain as of 2022: www.well.com/. It is interesting how Larry Page also liked The Grateful Dead as mentioned at The Google Story, his dad would take him to shows. Larry is a bit younger of course than the people in this documentary.
- 37 show McAfee
- 43:56: fantastic portrait of Cisco
Part 3 - Wiring the World:
- Berners-Lee at CERN and the invention of the URL.
- 1992: US Government allow commerce on the Internet
- Web browser history, Mosaic and Marc Andresseeen.
- 20:45: America Online
- 23:29: search engines and Excite. Google was a bit too small to be on his radar!
- 25:50: porn
- 27: The Motley Fool and advertising
- 30: Planet U grocery shopping
- 31:50: Amazon
- 33:00: immigrant workers, Indians playing cricket, outsourcing, Wipro Systems
- 41:25: Java
- 46:30: Microsoft joins the Internet. The Internet Tidal Wave Internet memo. Pearl Harbour day talk.
- 56:40: Excite Tour. If they had survived, they would have been Google with their quirky offices.
Open University Updated 2025-07-16
Not really dedicated to open source course material, nor to free courses...
The "Open" in its name only made sense in the 60's, when it was founded, nowadays, there isn't much about this institution that is very different compared to traditional Oxbridge. "Cheap more online university" would be a more adequate name for it.
A system that would truly live up to the name "Open" in the year 2020 is the one described at the ideal university by Ciro Santilli.
Wikipedia even says that the initial focus was on broadcasting learning material on television and radio, so what happened to that now that we have an even more powerful on-demand tool called Internet!
They even created their own MOOC website, FutureLearn. But www.freecodecamp.org/news/massive-open-online-courses-started-out-completely-free-but-where-are-they-now-1dd1020f59/ mentions:OMG. God why.
The course content is still free to access, but it’s only available for the duration of the course, and for two weeks after it ends.
A few open sources at: www.open.edu/openlearn/free-courses. The 5-hour course on particle physics says it all. Stated as of 2023 at www.open.ac.uk/about/open-educational-resources/openlearn/free-learning:
www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pj0rbafFBak What's an Open University Degree Like? by Luke Cutforth (2021) mentions that it is more autodidactic/online, and it encourages part time learning.
youtu.be/rsWwffX-u0A?t=99 Open University - How does it work? by Matt Greg Vlogs (2017) shows that they do have their own custom institutional material. And it is not open???? Please. youtu.be/rsWwffX-u0A?t=222 mentions that there is no entry exam, and you can change your courses at any time, that is good at least.
Israel apparently also created their own version in the 70's inspired by the British one: Open University of Israel. Same story it seems.
Ron Maimon Updated 2025-07-26
Ron Maimon is a male human theoretical physicist with an all but dissertation started in 1995 at Cornell University[ref][ref].
Ron Maimon's Physics Stack Exchange profile picture
. Source. Ron is mostly known for simultaneously:
- the amazing free online content he has published in online forums such as Stack Overflow and Quora, notably about particle physics, until around 2014 when Ron disappeared from the Internet entirely. Ciro Santilli figures he's hanging out with Ettore Majorana somewhere in the metaverse.
- having either been blocked from or quit every single website he participates in, partly due to his highly combative nature, e.g.:He explicitly defends this combative approach at youtu.be/ObXbKbpkSjQ?t=944 from Video 1. "Ron Maimon interview with Jeff Meverson (2014)":
- Physics Stack Exchange: physics.meta.stackexchange.com/users/4864/ron-maimon
physics.meta.stackexchange.com/questions/976/physics-ses-inability-to-deal-with-users-who-are-highly-persistent-have-kook-b user Marty Green makes one of the best characterizations of Ron's approach to science/collaboration:The thing about Ron Maimon is he definitely comes here to talk about physics. I personally can't get into discussions with him for two reasons: first, he's so single-minded in his own point of view that you can't really communicate with him back and forth; secondly, the structure of this forum is simply not conducive to extended discussions. But he sometimes posts things that are so coherently argued and with such intricate detail that even if I can't understand them myself, I just can't believe he's simply pulling this stuff out of his ass.
- physics.meta.stackexchange.com/questions/1376/what-violation-caused-this-suspension user Jerry Schirmer makes another good comment:
- Quora: www.quora.com/profile/Ron-Maimon. Ron was very active on Quora, until he was blocked for his views on the Boston Marathon bombing as mentioned at Video 1. "Ron Maimon interview with Jeff Meverson (2014)"
And notably, relevant to cirosantilli.com/china-dictatorship/stack-overflow-mods-refuse-to-clarify-if-anti-ccp-imagery-is-allowed-or-not-2021In order to have this process work [finding of truth] it is extremely important that the tone is hostile, that it is like a court of law, where you have an adversarial relationship with your opponent. Because if you have a friendly relationship with your opponent, then political consensus is preserved.
and he then also mentions that Wolfgang Pauli was a major proponent of this in physics, and so was Galileo.Unfortunately, when you're in a minority, the only way to correct the consensus view is to just shout it, and repeat it, until people go and look and check for themselves. The reason is that it creates an adversarial atmosphere where the people have to pick sides, and they don't like to pick sides, they would rather have everyone be happy. So when you have to pick sides, what do you do? You either butt out, you just leave it alone, you run away. Or you sit and review the evidence until you know which side to pick.
- Physics Stack Exchange: physics.meta.stackexchange.com/users/4864/ron-maimon
Ron seems to share a few philosophies which Ciro greatly agrees with as part of Cirism, which together with his knowledge of physics, make Ciro greatly respect Ron. Such philosophies include:
- he gives great importance to the history of physics and learning from original papers. He appears to know this insanely well, notably emphasizing that there is value in tutorials written by early pioneers of the field, see also Section "How to teach and learn physics". TODO find quote. Ciro Santilli distinctly remembers one specifically taking about this, but can't find it anymore.
- education views, notably emphasising autodidacticism
- www.quora.com/Why-should-high-school-students-learn-physics/answer/Ron-Maimon, highlighted at gmachine1729.livejournal.com/161418.html: "Why should high school students learn physics?" Answer:Yes, please, give it to me baby:
But they should learn it, preferably on their own, because the school doesn't know how to teach physics. Physics is extremely interesting, even the elementary kind. It takes the mathematics you learn in high school and uses it to describe certain natural phenomenon completely, beyond what was imagined possible in the wildest dreams of people like Pythagoras or Archimedes. If you have a computer, Newton's laws plus a tiny code can produce the motion of the planets around the sun, the motion of a free-twirling baton, the motion of colliding billiards, it's very simple.
- www.quora.com/Why-should-high-school-students-learn-physics/answer/Ron-Maimon, highlighted at gmachine1729.livejournal.com/161418.html: "Why should high school students learn physics?" Answer:
- enthusiasm for molecular biology technologies, seen e.g. at: www.quora.com/Why-are-an-abundance-of-physicists-moving-to-theoretical-biology/answer/Ron-Maimon on Quora:Ciro is actually specifically curious about whole cell simulation which he makes reference to.
[biology] is also clearly going to be the major technology of the 21st century, you should have a sugar outlet next to the electrical outlet, and plug in artificial biological technology made out of artificial cells. To plan these requires a complete method of describing biological cells, a precise model of all the processes, so that you can make artificial ones, and it produces a type of precise control on single-molecule chemistry that makes chemists drool.
- effortless effort and the to explain everything he knows online. These can be seen at www.quora.com/How-do-you-control-your-urge-to-access-the-internet-so-you-can-complete-your-assignments "How do you control your urge to access the Internet so you can complete your assignments?":
- his cheapness as in Ciro Santilli's cheapness as mentioned at youtu.be/ObXbKbpkSjQ?t=2454 from Video 1. "Ron Maimon interview with Jeff Meverson (2014)":Interviewer: there's a question on Quora where you say that you took a vow of poverty when you were very young.Ron: I was ten, I mean, most people would give it up, but I mean I figured I didn't have any need to give it up, so I just kept with it, I mean, I was never was really offered that much more. When we started the startup, I think I was offered 50k, but I said "no, I'll keep it 40k, I took a vow", and then they gave me 40k. And that of sort of set an example, the CEO also took 40k. It was a very good thing because we had very little money, we were a startup, and we were going by seed money.
However he also subscribes to some theories which Ciro Santilli considers conspiracy theories, e.g. his ideas about the Boston Marathon bombing that got him banned from Quora (a ban which Ciro strongly opposes due to freedom of speech concerns!), but the physics might be sound, Ciro Santilli does not know enough physics to judge, but it often feels that what he says makes sense.
chat.stackexchange.com/transcript/message/7104585#7104585 mentions that he was at Cornell University and did all but dissertation, but he mentions that he was still self-taught:This is corroborated e.g. at: web.archive.org/web/20201226171231/http://pages.physics.cornell.edu/~gtoombes/Student_Index.html (original pages.physics.cornell.edu/~gtoombes/Student_Index.html down as of 2023).
Eugene Seidel: On your personal info page you write that you are not a physics Ph.D. but does that mean you were a physics undergrad in college then went to grad school and finished ABD... or are you entirely self taught?Ron Maimon: ABD. I am self- taught though, I only went to school for accreditation. I had a thesis worth of work at the time I left grad-school,Eugene Seidel: ok thanksRon Maimon: I was just kind of sickened by academic stuff that was going on--- large extra dimensions were popular then.
At youtu.be/ObXbKbpkSjQ?t=2454 from Video 1. "Ron Maimon interview with Jeff Meverson (2014)" he mentions his brother is a professor. At physics.stackexchange.com/questions/32382/could-we-build-a-supercomputer-out-of-wires-and-switches-instead-of-a-microchip confirms that his brother's name is "Gaby Maimon", so this neuroscience professor at the Rockerfeller University is likely him: www.rockefeller.edu/our-scientists/heads-of-laboratories/985-gaby-maimon/. Looks, age, location and research interest match.
Some notable technical posts:
Some notable history posts:
- physics.stackexchange.com/questions/18632/good-book-on-the-history-of-quantum-mechanics/18643#18643 about the history of quantum mechanics give the quadratic explanation
- and closely related for the factor 2: physics.stackexchange.com/questions/27847/why-is-there-a-frac-1-2-in-frac-1-2-mv2/27916#27916
Bibliography:
- www.reddit.com/r/DecodingTheGurus/comments/17cb0n8/do_you_remember_ron_maimon_from_the_prepodcast/ "Do you remember Ron Maimon from the pre-podcast era? Where would he rank on the Guru scale?" user JohnFatherJohn comments:
I was actually friends with Ron Maimon at Cornell around 2006-2008. He was doing some research for my undergraduate research advisor and was a regular at a few of the same coffee shops I frequented. He was a legitimate brilliant physicist who had some strange personality quirks and blindspots, but his simultaneous breadth and depth of physics knowledge was staggering. He detested academia and couldn't stay focused on any one given problem for too long before moving on to something else though.
- gmachine1729.livejournal.com/161418.html Ron Maimon answers about physics and math on Quora (part 1) by Sheng Li (2020) contains a selection of some amazing Ron Maimon posts
- www.reddit.com/r/RonMaimon/ someone made a Reddit for him. Less than 100 users as of 2022, but has potential.
- some Quora threads about him, oh the irony:
- www.quora.com/Is-Ron-Maimon-actually-a-pioneer-or-a-jest
- www.quora.com/Are-Ron-Maimons-answers-on-mathematics-physics-and-computer-science-factually-correct
- www.quora.com/What-do-people-think-of-Ron-Maimons-paper-Computational-Theory-of-Biological-Function-I
- www.quora.com/Who-is-Ron-Maimon/answer/Ron-MaimonAlso in a comment he explains something to a now deleted comment, presumably asking why he dropped out of grad school, and gives a lot more insight:
I'm a physics grad school drop-out working in theoretical biology but I still do physics when I get a chance, but not right now because I am in a middle of a project to understand the properties of a certain virus as completely as possible.
I dropped out mainly to do biology with friends at a startup, because I figured out how you're supposed to do theory in biology, but also I truly believe it was next to impossible for me to get a degree without selling out, and I would rather be shot than write a paper with an idea I don't believe.My grad school phase was a disaster. I first worked for Eric Siggia, but I got away because he had me do something boring and safe, I figured I have only a limited number of years before I turn 30 and my brain rots, and I wasn't going to sell out and do second-rate stuff. I found a young guy at the department doing interesting things (Siggia was also doing interesting things, like RNA interactions, he just wouldn't assign any of them to ME), this was Philip Argyres, and got him to take me. Argyres wanted me to work on large-extra dimensions (this was 1998), but I made it clear to him that I would rather be boiled in oil. I worked a little bit on a crappy experimental setup that didn't work at all, because I didn't know enough about electromagnetic screening nor about how to set up experiment. But EVERYONE LOVED IT! This is also how I knew it was shit. Good work is when everyone hates it. But I learned Lifschitz's ideas for quantum electrodynamics in media from this project.Me and every competent young person in high-energy physics knew large extra dimensions was a fraud on the day it came out, and I had no intention of doing anything except killing the theory. Once Wikipedia appeared, I did my best to kill it by exposing it's charlatanry on the page for large extra dimension. That was in 2005 (after getting fired from the company), and from this point onward large-extra-dimensions lost steam. But I can't tell how much of this was my doing.Argyres liked N=2 theory, and we did something minor in N=2 SUSY models around 2000, but I was bogged down here, because I was trying to do Nicolai map for these, and it ALMOST worked for years, but it never quite worked. But I knew from the moduli interpretation and Seiberg-Witten solution that it must work. If I live long enough, I'll figure it out, I am still sure it isn't hard. But this was the link to statistical stochastic models, the work I was doing with Jennifer Schwarz, and I wanted to link up the two bodies of work (they naturally do through Nicolai map).But I had my own discovery, the first real discovery I made, in 1999, this thing that I called the mass-charge inequality, what Vafa and Motl called "the weakest-force principle" when they discovered it in 2006. It was swampland, and Vafa hadn't yet begun swampland. My advisor didn't believe my result was correct, because he saw me say many stupid things before this. So he wouldn't write it or develop it with me (but I had read about Veltman telling 'tHooft he couldn't publish the beta-function, I knew Argyres was wrong about this)Anyway, Argyres left for Cincinnatti in 2000, and I joined the company then. I was in the company until january 2005. Then they fired me, which was ok, by then it was a miserable hell-hole full of business types.I discovered Wikipedia, and started killing large extra dimensions. I wanted to finish my thesis, and some people agreed to help me do this, but I had told myself "no thesis until you get the Nicolai map sorted out" and I never did. I worked with Chris Henley a little bit, who wanted me to do some stuff for him, and I discovered an interesting model for high-Tc, but Henley said it was out of fasion, and nobody would care, even though I knew it was the key to the phenomenon (still unpublished, but soon).This was 2008-2009, and I became obsessed with cold fusion, so Henley dropped me, as I had clearly gone crazy. I developed the theory of cold fusion during the last weeks of working for Henley. Then I dropped out for good.Honestly, by the time I was gone, I realized that the internet would make a degree counterproductive, because I knew I had better internet writing skills than any of the old people, I was a Usenet person. Online, the degrees and accreditation were actually a hinderance. So by this point, I secretly preferred not to have a PhD, because I knew I was good at physics, and I could attack from the outside and win. It's not too hard if you know the technical material.The only problem is that I was unemployed and isolated in Ithaca for about 7 years after having gone through my first productive phase. But I developed the cold-fusion ideas in this period, I learned a lot of mathematics, and I developed a ton of biology ideas that are mostly unpublished, but will be published soon. It astonished people that I could have no degree and be unemployed and have such a sky-high ego. The reason is that I could evaluate my own stuff, and I liked it!
Other possible accounts:
Backlinks:
- 2022: twitter.com/johncarlosbaez/status/1556085484937310209 by John Baez. This page was one of the top Google hits for "Ron Maimon" at the time.
Ron Maimon interview with Jeff Meverson (2014)
Source. Ripped from Jeff's "Quoracast": player.fm/series/quoracast-podcast/ron-maimon-truther Ron mentions he was an early-Usenet user. Key points:- youtu.be/ObXbKbpkSjQ?t=2247 mentions that there is a question on Quora where Ron said he took a vow of poverty when he was 10. This reminded Ciro of Ciro Santilli's cheapness.
- youtu.be/ObXbKbpkSjQ?t=2532 mentions his admiration for Leonard Susskind, in particular him starting out as a plumber
- youtu.be/ObXbKbpkSjQ?t=3088Ron: no, no, I'll just go and do, library, write some papers or whatever. This is not, and this is not like... basically, look, I wrote most of what I wanted to write on Quora anyway. I have gotten almost everything out of my system. I wanted to write, a couple of other things, but they weren't major.
School must offer free accommodation for students Created 2024-11-15 Updated 2025-07-16
More precisely, for students whose parents don't live near the school. Or alternatively, online-only courses that offer the same diploma as the presencial version. Or a compromise where the best N% students get accommodation, where N is a parameter of how decent your society is overall.
Since all the learning resources will be available online on OurBigBook.com, or through online 1-to-1 chats with mentors, it might be cheaper for students to work either from their parent's homes if their home has reasonable work conditions: a silent room with reasonable Internet access and no drug addicts in the house.
Alternatively, a public local library with free WiFi would do as well. But there would need to be a strict silence policy enforced, unlike most public libraries we see today. Ciro once saw a bird shaped noise detector that would sing if the noise went above a certain threshold, that was a good idea. Just like linting, it is easier to let machines decide deterministically on subjective questions to reduce useless arguments over who is right. Ciro has even seen libraries where the local council uses the same library open space as a citizen counsel area. What's the fucking point... these people have never done any deep work in their lives.
Then the state only needs to pay transportation and temporary accommodation to attend concentrated month-long laboratory workshop courses and week-long conferences, since the only reason for universities to exist should be the laboratories. In cases where the home conditions are not good enough, the state can either pay for on-demand WeWork-like offices near the student's home, of for a full on-campus accommodation as in a boarding school. What is indispensable is that all students who pass the entry criteria must have such working conditions. Students who stay home can also earn a scholarship to help pay for their rent, food and Internet access.
Anything else is just incredibly unfair to the poor. Ciro Santilli has already witnessed two cases, in developed, and under-developed countries, where very high potential poorer students were forced to work to support themselves in parallel to a demanding degree because their parents couldn't pay their rent on a different city, and the students mental health issues due to this. In one of those cases the student had to abandon the course altogether.
It doesn't help that school has become a pure student-evaluation system, which basically implies putting studets through a lot of useless pressure.
One of the stories that Ciro Santilli's father tells is about how when they were dating, one of Ciro Santilli's mother's greatest wish for her hypotetical child would be that "they should not need to work during their studies as she had". As destiny would have it, Ciro Santilli's family had good conditions and Ciro never thought even once about money. And even then, school still sucked. Imagine without that basic, mandatory, stability!
Superconductor I-V curve Updated 2025-07-16
Symmetric encryption Created 2024-10-12 Updated 2025-07-16
Symmetric encryption is a type of encryption where you use a password (also known as a "key") to encrypt your data, and then the same password to decrypt the data.
For example, this is the type of encryption that is used for encrypting the data in our smartphones and laptops with disk encryption.
This way, if your laptop gets stolen, the thief is not able to see your private photos without knowing your password, even though they are able to read every byte of your disk.
The downside is that that you have to type your password every time you want to login. This leads people to want to use shorter passwords, which in turn are more prone to password cracking.
The other main type of encryption is public-key cryptography.
The advantage of public-key cryptography is that it allows you to send secret messages to other people even an the attacker is able to capture the encrypted messages. This is for example what you want to do when sending a personal message to a friend over the Internet. Such encryption is especially crucial when using wireless communication such as Wi-Fi, where anyone nearby can capture the signals you send and receive, and would be able to read all your data if it weren't encrypted.
Easily sending encrypted messages over the Internet is not possible with symmetric encryption because for your friend to decrypt the message in that system, you'd need to send them the password, which the attacker would also be able to eavesdrop and then decrypt the message that follows using it. The problem of sharing a password with another person online is called key exchange.
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is one of the most popular families of symmetric encryption algorithms.
OpenSSL is a popular open source implementation of symmetric and public-key cryptography. A simple example of using OpenSSL for symmetric encryption from the command-line is:This asks for a password, which we set as contains:Then to decrypt:once again asks for your password and given the correct password produces a file This was tested on Ubuntu 24.04, OpenSSL 3.0.13. See also: How to use OpenSSL to encrypt/decrypt files? on Stack Overflow.
echo 'Hello World!' > message.txt
openssl aes-256-cbc -a -salt -pbkdf2 -in message.txt -out message.txt.encasdfqwer, and then produces a file message.txt.enc containing garbled text such that:hd message.txt.enc00000000 55 32 46 73 64 47 56 6b 58 31 38 58 48 65 2f 30 |U2FsdGVkX18XHe/0|
00000010 70 56 42 2b 70 45 6c 55 59 38 2b 54 38 7a 4e 34 |pVB+pElUY8+T8zN4|
00000020 4e 37 6d 52 2f 73 6d 4d 62 64 30 3d 0a |N7mR/smMbd0=.|
0000002dopenssl aes-256-cbc -d -a -pbkdf2 -in message.txt.enc -out message.new.txtmessage.new.txt containing the original message:Hello World!There is no provably secure symmetric-key algorithm besides the one-time pad, which has the serious drawback of requiring the key to be as long as the message. This means that we believe that most encryption algorithms are secure because it is a hugely valuable target and no one has managed to crack them yet. But we don't have a mathematical proof that they are actually secure, so they could in theory be broken by new algorithms one day.
The bullying of young Ciro Santilli Updated 2025-07-16
Ciro was even more stupid than as of 2020, and continued to try and hang out with those evil kids to show them he was cool too or that he was strong, and so continued to get hurt.
Advice to his children: stay away from evil people.
The bullied sometimes feels an almost masochistic desire to overcome the bullies' contempt, and to try and either become friends with the bullies, or to overpower them.
You must never give into those thoughts.
If you come across evil people, smile a fake smile to them, and walk away, but never give your back to them, and always be ready to fight.
If they laugh at you, know that you are shit like everyone else, pretend to laugh with them, take their post and repost it on your public profile, and silently stay away from those idiots.
Never show any weakness.
If a fight is likely, always be ready, always have your friends nearby, be as well armed as the enemy, and never be outnumbered.
On the Internet, never care about e-bully posts, either block them immediately, and anyone that likes their posts, or follow Ciro's reply policy.
Call parents or other authorities as soon as there is risk of physical harm. Better a living free pussy than dead or in youth detention for murder. Similar advice applies if you are going to jail I guess.
If a physical fight is inevitable however, ignore Jesus this once and don't give the other face, but rather follow the Talmud and fight all out on the beaches:References:
If someone comes to kill you, rise and kill first.
The Sikh knife, the Kirpan, which Sikhs must carry at all times as a religious obligation, also comes to mind. The Sikh must have been bullied out of the their minds at some point in history, Ciro understands.
Non-violence only works when you have bodies to spare from your followers.
Perhaps it was good to learn those lessons early, before the stakes were too high. Adults fake it much better, and therefore it is harder to learn those lessons from them, but they are still just as evil on the inside.
These experiences might have contributed to Ciro Santilli's self perceived compassionate personality.
University entry exam Updated 2025-07-16
They mean that until you are 18, you have to study a bunch of generic crap you hate just to get into university. Rather than studying whatever it is that you truly love to become a God at it as fast as possible and have any chance of advancing the field.
And then, if you decide that you want to change, which is not unlikely since you haven't really try to study what you signed up for before then, it can be very hard and time consuming, leading to a bunch of adults with useless degress they will never use at work.
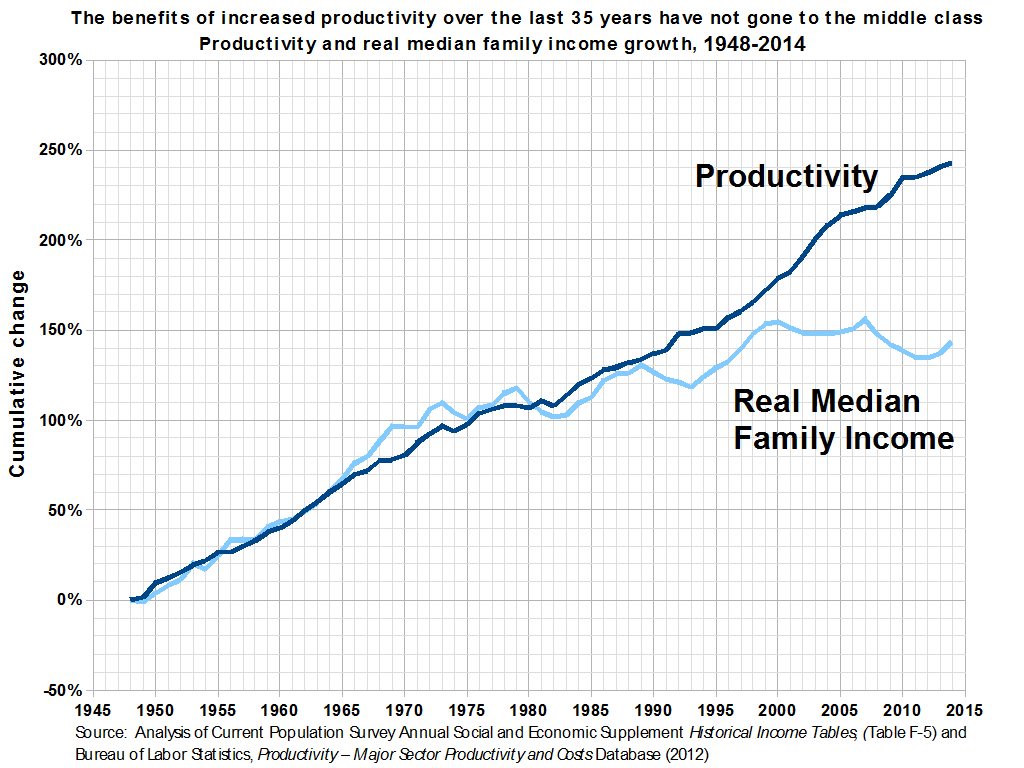
Wealth distribution in the United States Updated 2025-07-16
www.cbpp.org/wealth-concentration-has-been-rising-toward-early-20th-century-levels-2 shows historical for top 1% and 0.5% from 1920 to 2010.
TODO why is it so hard to find a proper cumulative distribution function-like curve? OMG. This appears to be also called a Lorenz curve.
Wealth Inequality in America by politizane
. Source. When in doubt, choose the course that has the most experimental work Updated 2025-07-16
And above all, you can always learn software engineering later on for free, because the programming community is so much more open than any other so far, notably e.g. with Stack Overflow and GitHub, see also: Section "Ciro Santilli's Open Source Enlightenment". Ciro Santilli is trying to change that with OurBigBook.com, but don't hold your breath. But it is increasingly hard to understand why there isn't an university that forces teachers to publish all their notes and lecture videos (which should be mandatorily recorded) with a Creative Commons License, and then let anyone take whichever exams they want for a small fee or for free.
Actually, there is a good chance you will learn to program, like it or not, because chances are that you won't be able to find as decent a job doing anything else.
But there is one thing you cannot learn for free: laboratory work. Laboratory work is just too expensive to carry out outside of an institution.
Basically, if you don't do laboratory work in undergrad, you will very likely never be able to do so in your entire life.
Because laboratories are so rare and expensive, it is laboratories that put you in the best most unfair position at creating world changing deep tech startups, which is why when in doubt, choose the course that has the most experimental work. Yes, you won't be able to achieve those insanely concentrated equities of the early-Internet, as you will need more venture capital to run your company, but those days are over now, deal with it.