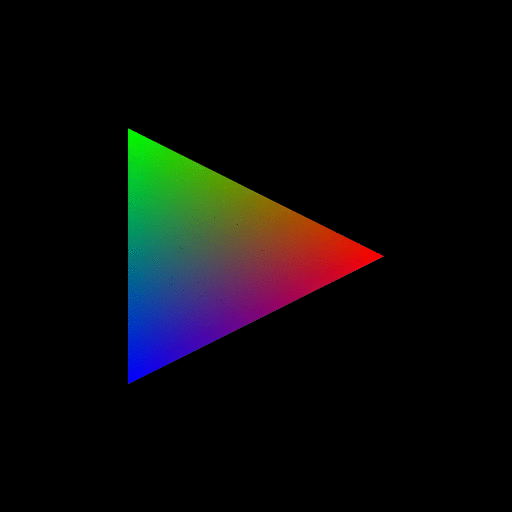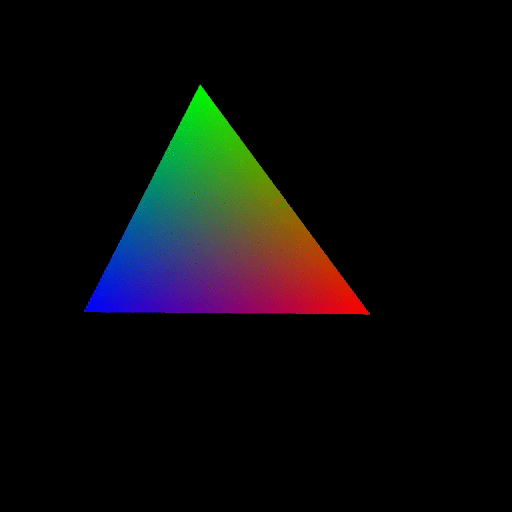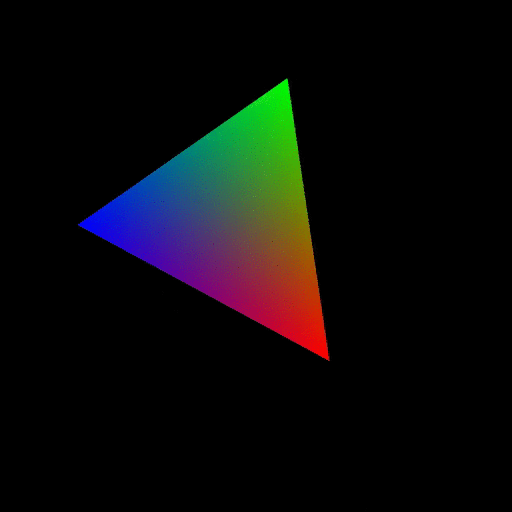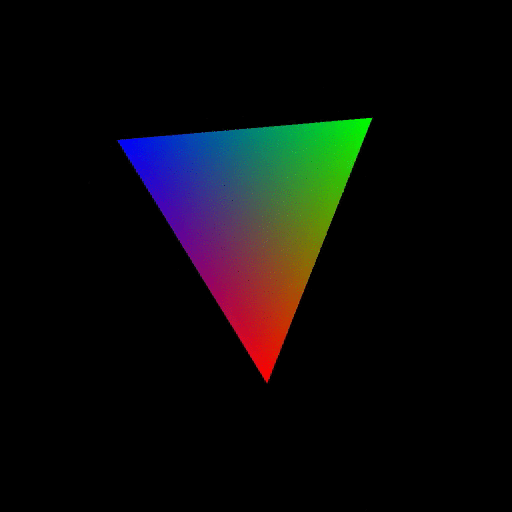The best articles by Ciro Santilli Updated 2025-07-16
These are the best articles ever authored by Ciro Santilli, most of them in the format of Stack Overflow answers.
Ciro posts update about new articles on his Twitter accounts.
Some random generally less technical in-tree essays will be present at: Section "Essays by Ciro Santilli".
- Trended on Hacker News:
- CIA 2010 covert communication websites on 2023-06-11. 190 points, a mild success.
- x86 Bare Metal Examples on 2019-03-19. 513 points. The third time something related to that repo trends. Hacker news people really like that repo!
- again 2020-06-27 (archive). 200 points, repository traffic jumped from 25 daily unique visitors to 4.6k unique visitors on the day
- How to run a program without an operating system? on 2018-11-26 (archive). 394 points. Covers x86 and ARM
- ELF Hello World Tutorial on 2017-05-17 (archive). 334 points.
- x86 Paging Tutorial on 2017-03-02. Number 1 Google search result for "x86 Paging" in 2017-08. 142 points.
- x86 assembly
- What does "multicore" assembly language look like?
- What is the function of the push / pop instructions used on registers in x86 assembly? Going down to memory spills, register allocation and graph coloring.
- Linux kernel
- What do the flags in /proc/cpuinfo mean?
- How does kernel get an executable binary file running under linux?
- How to debug the Linux kernel with GDB and QEMU?
- Can the sys_execve() system call in the Linux kernel receive both absolute or relative paths?
- What is the difference between the kernel space and the user space?
- Is there any API for determining the physical address from virtual address in Linux?
- Why do people write the
#!/usr/bin/envpython shebang on the first line of a Python script? - How to solve "Kernel Panic - not syncing: VFS: Unable to mount root fs on unknown-block(0,0)"?
- Single program Linux distro
- QEMU
- gcc and Binutils:
- How do linkers and address relocation works?
- What is incremental linking or partial linking?
- GOLD (
-fuse-ld=gold) linker vs the traditional GNU ld and LLVM ldd - What is the -fPIE option for position-independent executables in GCC and ld? Concrete examples by running program through GDB twice, and an assembly hello world with absolute vs PC relative load.
- How many GCC optimization levels are there?
- Why does GCC create a shared object instead of an executable binary according to file?
- C/C++: almost all of those fall into "disassemble all the things" category. Ciro also does "standards dissection" and "a new version of the standard is out" answers, but those are boring:
- What does "static" mean in a C program?
- In C++ source, what is the effect of
extern "C"? - Char array vs Char Pointer in C
- How to compile glibc from source and use it?
- When should
static_cast,dynamic_cast,const_castandreinterpret_castbe used? - What exactly is
std::atomicin C++?. This answer was originally more appropriately entitled "Let's disassemble some stuff", and got three downvotes, so Ciro changed it to a more professional title, and it started getting upvotes. People judge books by their covers. notmain.o 0000000000000000 0000000000000017 W MyTemplate<int>::f(int) main.o 0000000000000000 0000000000000017 W MyTemplate<int>::f(int)Code 1.. From: What is explicit template instantiation in C++ and when to use it?nmoutputs showing that objects are redefined multiple times across files if you don't use template instantiation properly
- IEEE 754
- What is difference between quiet NaN and signaling NaN?
- In Java, what does NaN mean?
Without subnormals: +---+---+-------+---------------+-------------------------------+ exponent | ? | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | +---+---+-------+---------------+-------------------------------+ | | | | | | v v v v v v ----------------------------------------------------------------- floats * **** * * * * * * * * * * * * ----------------------------------------------------------------- ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ | | | | | | 0 | 2^-126 2^-125 2^-124 2^-123 | 2^-127 With subnormals: +-------+-------+---------------+-------------------------------+ exponent | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | +-------+-------+---------------+-------------------------------+ | | | | | v v v v v ----------------------------------------------------------------- floats * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * ----------------------------------------------------------------- ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ | | | | | | 0 | 2^-126 2^-125 2^-124 2^-123 | 2^-127Code 2.Visualization of subnormal floating point numbers vs what IEEE 754 would look like without them. From: What is a subnormal floating point number?
- Computer science
- Algorithms
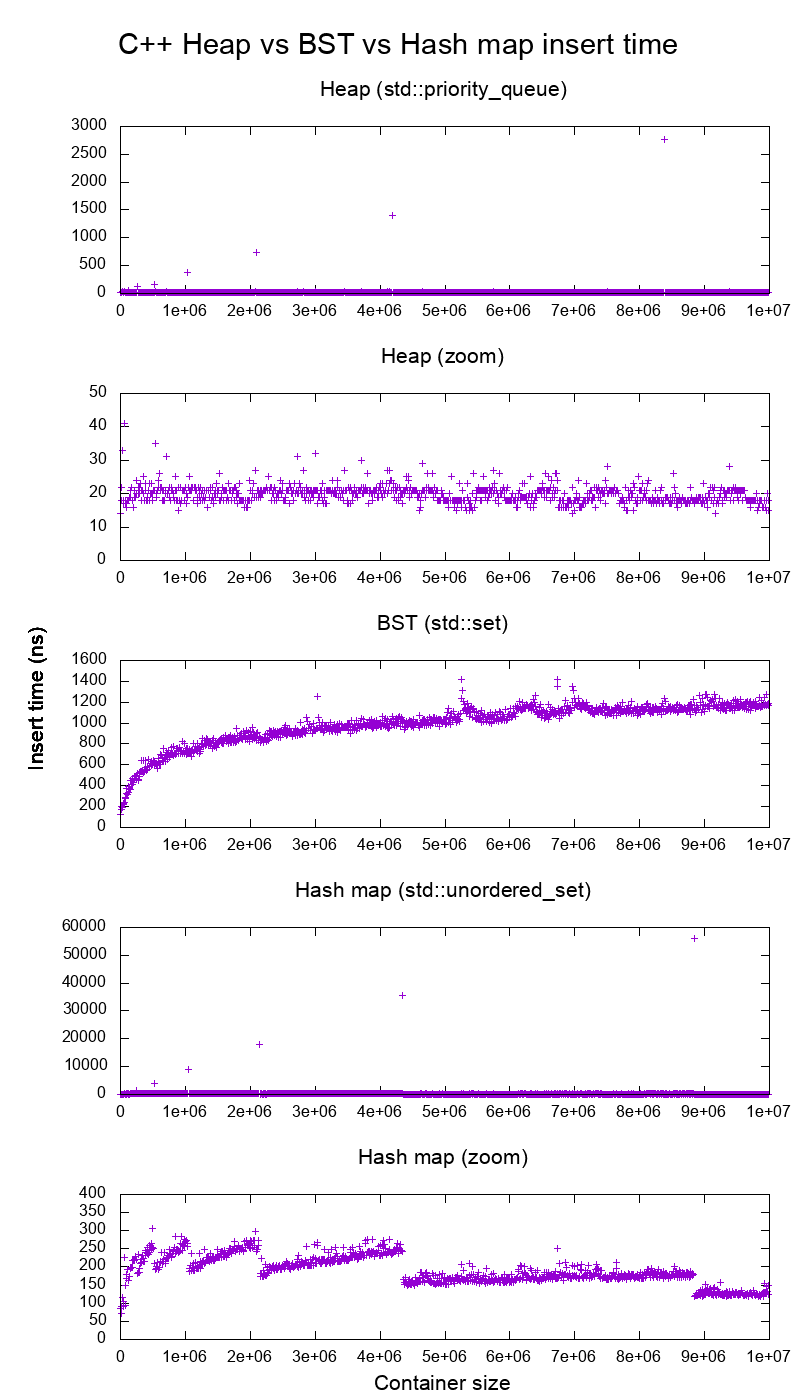
Figure 5. Average insertion time into heaps, binary search tree and hash maps of the C++ standard library. Source. From: Heap vs Binary Search Tree (BST)
- Is it necessary for NP problems to be decision problems?
- Polynomial time and exponential time. Answered focusing on the definition of "exponential time".
- What is the smallest Turing machine where it is unknown if it halts or not?. Answer focusing on "blank tape" initial condition only. Large parts of it are summarizing the Busy Beaver Challenge, but some additions were made.
- Algorithms
- Git
| 0 | 4 | 8 | C | |-------------|--------------|-------------|----------------| 0 | DIRC | Version | File count | ctime ...| 0 | ... | mtime | device | 2 | inode | mode | UID | GID | 2 | File size | Entry SHA-1 ...| 4 | ... | Flags | Index SHA-1 ...| 4 | ... |Code 3.ASCII art depicting the binary file format of the Git index file. From: What does the git index contain EXACTLY?tree {tree_sha} {parents} author {author_name} <{author_email}> {author_date_seconds} {author_date_timezone} committer {committer_name} <{committer_email}> {committer_date_seconds} {committer_date_timezone} {commit message}Code 4.Description of the Git commit object binary data structure. From: What is the file format of a git commit object data structure?- How do I clone a subdirectory only of a Git repository?
- Python
- Web technology
- OpenGL
Figure 7. OpenGL rendering output dumped to a GIF file. Source. From: How to use GLUT/OpenGL to render to a file?- What are shaders in OpenGL?
- Why do we use 4x4 matrices to transform things in 3D?
Figure 10. Sinusoidal circular wave heatmap generated with an OpenGL shader at 60 FPS on SDL. Source.
- Node.js
- Ruby on Rails
- POSIX
- What is POSIX? Huge classified overview of the most important things that POSIX specifies.
- Systems programming
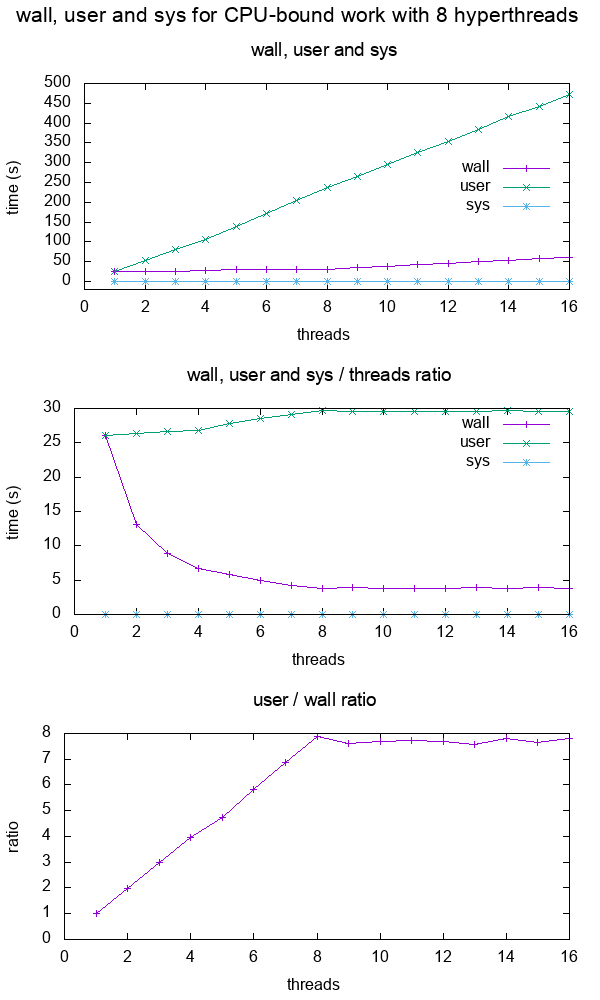
- What do the terms "CPU bound" and "I/O bound" mean?
Figure 12. Plot of "real", "user" and "sys" mean times of the output of time for CPU-bound workload with 8 threads. Source. From: What do 'real', 'user' and 'sys' mean in the output of time?+--------+ +------------+ +------+ | device |>---------------->| function 0 |>----->| BAR0 | | | | | +------+ | |>------------+ | | | | | | | +------+ ... ... | | |>----->| BAR1 | | | | | | +------+ | |>--------+ | | | +--------+ | | ... ... ... | | | | | | | | +------+ | | | |>----->| BAR5 | | | +------------+ +------+ | | | | | | +------------+ +------+ | +--->| function 1 |>----->| BAR0 | | | | +------+ | | | | | | +------+ | | |>----->| BAR1 | | | | +------+ | | | | ... ... ... | | | | | | +------+ | | |>----->| BAR5 | | +------------+ +------+ | | | ... | | | +------------+ +------+ +------->| function 7 |>----->| BAR0 | | | +------+ | | | | +------+ | |>----->| BAR1 | | | +------+ | | ... ... ... | | | | +------+ | |>----->| BAR5 | +------------+ +------+Code 5.Logical struture PCIe device, functions and BARs. From: What is the Base Address Register (BAR) in PCIe?
- Electronics
- Raspberry Pi
Figure 13. Raspberry Pi 2 directly connected to a laptop with an Ethernet cable. Image from answer to: How to hook up a Raspberry Pi via Ethernet to a laptop without a router?Figure 14. . Image from answer to: How to hook up a Raspberry Pi via Ethernet to a laptop without a router? Figure 15. . Image from answer to: How to emulate the Raspberry Pi 2 on QEMU? Figure 16. Bare metal LED blinker program running on a Raspberry Pi 2. Image from answer to: How to run a C program with no OS on the Raspberry Pi?
- Raspberry Pi
- Computer security
- Media
Video 2. Canon in D in C. Source.The original question was deleted, lol...: How to programmatically synthesize music?- How to resize a picture using ffmpeg's sws_scale()?
- Is there any decent speech recognition software for Linux? ran a few examples manually on
vosk-apiand compared to ground truth.
- Eclipse
- Computer hardware
- Scientific visualization software
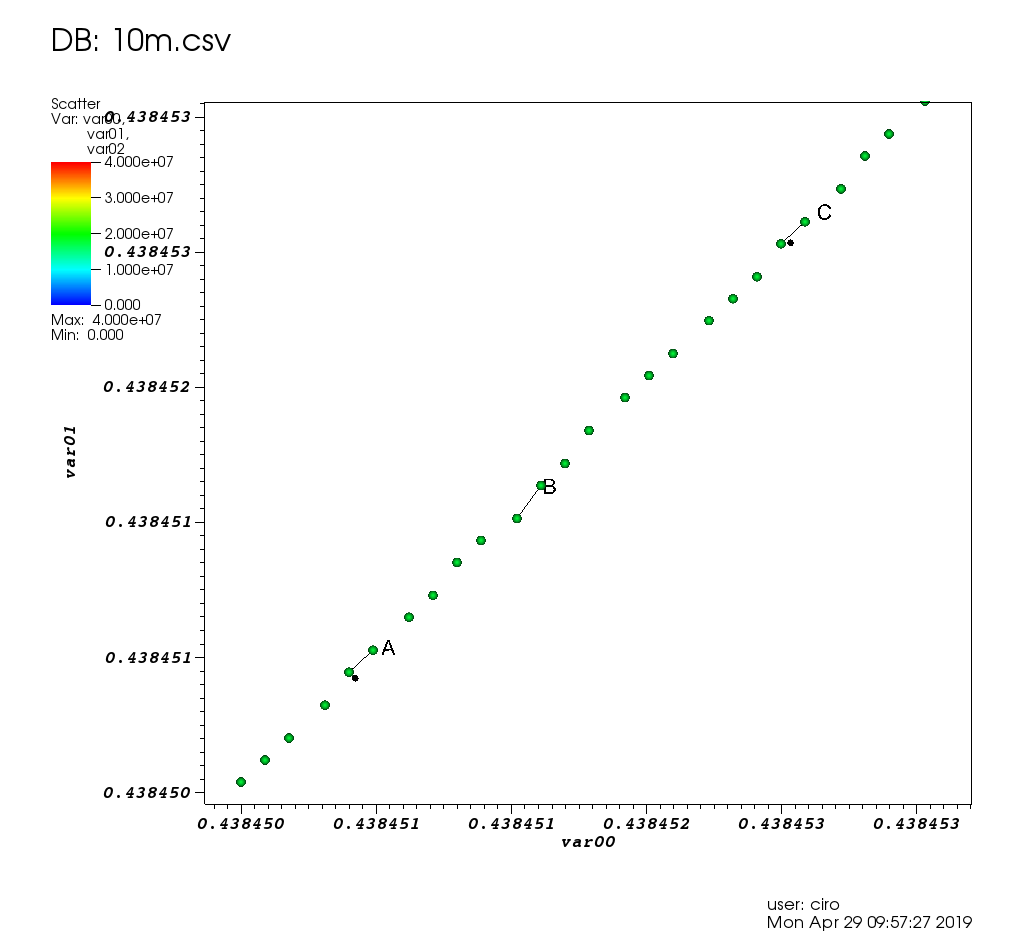
Figure 17. VisIt zoom in 10 million straight line plot with some manually marked points. Source. From: Section "Survey of open source interactive plotting software with a 10 million point scatter plot benchmark by Ciro Santilli"
- Numerical analysis
- Computational physics
- Register transfer level languages like Verilog and VHDL
- Verilog:
Figure 19. . See also: Section "Verilator interactive example"
- Verilog:
- Android
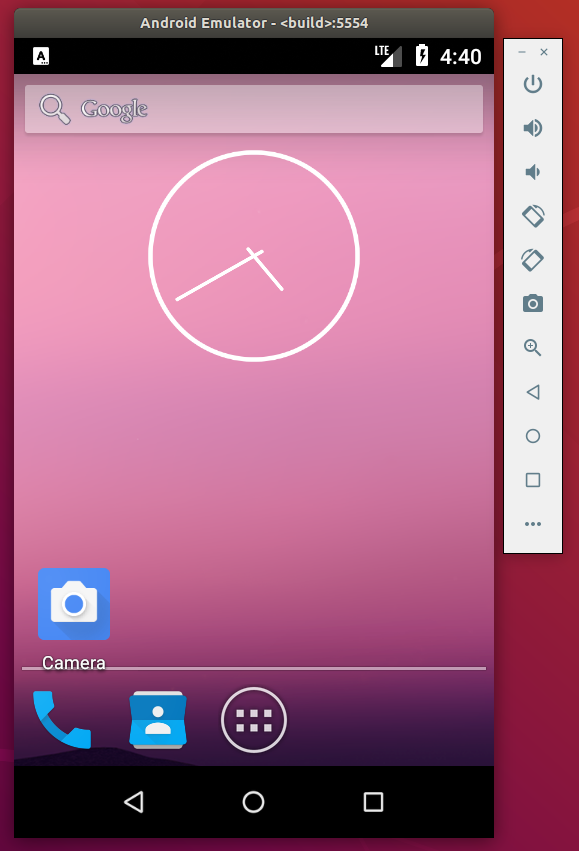
Video 4. Android screen showing live on an Ubuntu laptop through ADB. Source. From: How to see the Android screen live on an Ubuntu desktop through ADB?
- Debugging
- Program optimization
- What is tail call optimization?
Figure 21. . Source. The answer compares gprof, valgrind callgrind, perf and gperftools on a single simple executable.
- Data
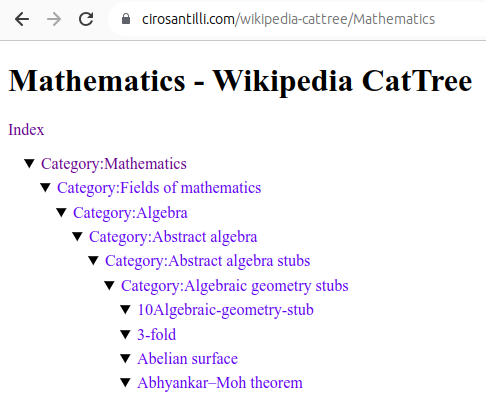
Figure 22. Mathematics dump of Wikipedia CatTree. Source. In this project, Ciro Santilli explored extracting the category and article tree out of the Wikipedia dumps.
- Mathematics
Figure 23. Diagram of the fundamental theorem on homomorphisms by Ciro Santilli (2020)Shows the relationship between group homomorphisms and normal subgroups.- Section "Formalization of mathematics": some early thoughts that could be expanded. Ciro almost had a stroke when he understood this stuff in his teens.
Figure 24. Simple example of the Discrete Fourier transform. Source. That was missing from Wikipedia page: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Discrete_Fourier_transform!
- Network programming
- Physics
- What is the difference between plutonium and uranium?
Figure 25. Spacetime diagram illustrating how faster-than-light travel implies time travel. From: Does faster than light travel imply travelling back in time?
- Biology
Figure 26. Top view of an open Oxford Nanopore MinION. Source. From: Section "How to use an Oxford Nanopore MinION to extract DNA from river water and determine which bacteria live in it"Figure 27. Mass fractions in a minimal growth medium vs an amino acid cut in a simulation of the E. Coli Whole Cell Model by Covert Lab. Source. From: Section "E. Coli Whole Cell Model by Covert Lab"
- Quantum computing
- Section "Quantum computing is just matrix multiplication"
Figure 28. Visualization of the continuous deformation of states as we walk around the Bloch sphere represented as photon polarization arrows. From: Understanding the Bloch sphere.
- Bitcoin
- GIMP
Figure 29. GIMP screenshot part of how to combine two images side-by-side in GIMP?
- Home DIY
Figure 30. Total_Blackout_Cassette_Roller_Blind_With_Curtains.Source. From: Section "How to blackout your window without drilling"
- China
CIDARLAB/cello Updated 2025-07-16
Design software for synthetic biological circuit.
The input is in Verilog! Overkill?
Closed standard Updated 2025-07-16
How the hell are you supposed to develop an open source implementation of something that has a closed standard?
Electronic design automation Updated 2025-07-16
A set of software programs that compile high level register transfer level languages such as Verilog into something that a fab can actually produce. One is reminded of a compiler toolchain but on a lower level.
The most important steps of that include:
- logic synthesis: mapping the Verilog to a standard cell library
- place and route: mapping the synthesis output into the 2D surface of the chip
Logic synthesis Updated 2025-07-16
Step of electronic design automation that maps the register transfer level input (e.g. Verilog) to a standard cell library.
Quantum circuit description language Updated 2025-07-16
One would hope that they are not Turing complete, this way they may serve as a way to pass on data in such a way that the receiver knows they will only be doing so much computation in advance to unpack the circuit. So it would be like JSON is for JavaScript.
Register transfer level Updated 2025-07-16
Register transfer level is the abstraction level at which computer chips are mostly designed.
The only two truly relevant RTL languages as of 2020 are: Verilog and VHDL. Everything else compiles to those, because that's all that EDA vendors support.
Much like a C compiler abstracts away the CPU assembly to:
- increase portability across ISAs
- do optimizations that programmers can't feasibly do without going crazy
Source code leaks Updated 2025-07-16
Verilator Updated 2025-07-16
One very good thing about this is that it makes it easy to create test cases directly in C++. You just supply inputs and clock the simulation directly in a C++ loop, then read outputs and assert them with
assert(). And you can inspect variables by printing them or with GDB. This is infinitely more convenient than doing these IO-type tasks in Verilog itself.Some simulation examples under verilog.
First install Verilator. On Ubuntu:Tested on Verilator 4.038, Ubuntu 22.04.
sudo apt install verilatorRun all examples, which have assertions in them:
cd verilator
make runFile structure is for example:
- verilog/counter.v: Verilog file
- verilog/counter.cpp: C++ loop which clocks the design and runs tests with assertions on the outputs
- verilog/counter.params: gcc compilation flags for this example
- verilog/counter_tb.v: Verilog version of the C++ test. Not used by Verilator. Verilator can't actually run out
_tbfiles, because they do in Verilog IO things that we do better from C++ in Verilator, so Verilator didn't bother implementing them. This is a good thing.
Example list:
- verilog/negator.v, verilog/negator.cpp: the simplest non-identity combinatorial circuit!
- verilog/counter.v, verilog/counter.cpp: sequential hello world. Synchronous active high reset with active high enable signal. Adapted from: www.asic-world.com/verilog/first1.html
- verilog/subleq.v, verilog/subleq.cpp: subleq one instruction set computer with separated instruction and data RAMs
Verilator interactive example Updated 2025-07-16
The example under verilog/interactive showcases how to create a simple interactive visual Verilog example using Verilator and SDL.
You could e.g. expand such an example to create a simple (or complex) video game for example if you were insane enough. But please don't waste your time doing that, Ciro Santilli begs you.
The example is also described at: stackoverflow.com/questions/38108243/is-it-possible-to-do-interactive-user-input-and-output-simulation-in-vhdl-or-ver/38174654#38174654
Usage: install dependencies:then run as either:Tested on Verilator 4.038, Ubuntu 22.04.
sudo apt install libsdl2-dev verilatormake run RUN=and2
make run RUN=moveFile overview: