Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase Updated 2025-07-16
Binds an amino acid to the correct corresponding tRNA sequence. Wikipedia mentions that humans have 20 of them, one for each proteinogenic amino acid.
The best articles by Ciro Santilli Updated 2025-07-16
These are the best articles ever authored by Ciro Santilli, most of them in the format of Stack Overflow answers.
Ciro posts update about new articles on his Twitter accounts.
Some random generally less technical in-tree essays will be present at: Section "Essays by Ciro Santilli".
- Trended on Hacker News:
- CIA 2010 covert communication websites on 2023-06-11. 190 points, a mild success.
- x86 Bare Metal Examples on 2019-03-19. 513 points. The third time something related to that repo trends. Hacker news people really like that repo!
- again 2020-06-27 (archive). 200 points, repository traffic jumped from 25 daily unique visitors to 4.6k unique visitors on the day
- How to run a program without an operating system? on 2018-11-26 (archive). 394 points. Covers x86 and ARM
- ELF Hello World Tutorial on 2017-05-17 (archive). 334 points.
- x86 Paging Tutorial on 2017-03-02. Number 1 Google search result for "x86 Paging" in 2017-08. 142 points.
- x86 assembly
- What does "multicore" assembly language look like?
- What is the function of the push / pop instructions used on registers in x86 assembly? Going down to memory spills, register allocation and graph coloring.
- Linux kernel
- What do the flags in /proc/cpuinfo mean?
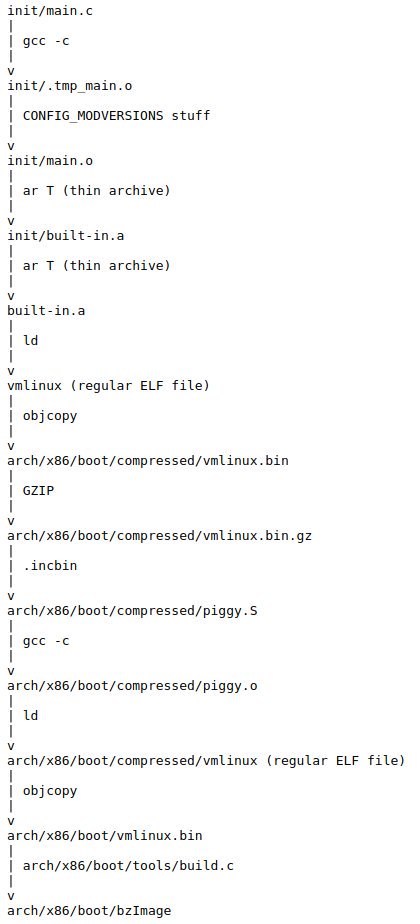
- How does kernel get an executable binary file running under linux?
- How to debug the Linux kernel with GDB and QEMU?
- Can the sys_execve() system call in the Linux kernel receive both absolute or relative paths?
- What is the difference between the kernel space and the user space?
- Is there any API for determining the physical address from virtual address in Linux?
- Why do people write the
#!/usr/bin/envpython shebang on the first line of a Python script? - How to solve "Kernel Panic - not syncing: VFS: Unable to mount root fs on unknown-block(0,0)"?
- Single program Linux distro
- QEMU
- gcc and Binutils:
- How do linkers and address relocation works?
- What is incremental linking or partial linking?
- GOLD (
-fuse-ld=gold) linker vs the traditional GNU ld and LLVM ldd - What is the -fPIE option for position-independent executables in GCC and ld? Concrete examples by running program through GDB twice, and an assembly hello world with absolute vs PC relative load.
- How many GCC optimization levels are there?
- Why does GCC create a shared object instead of an executable binary according to file?
- C/C++: almost all of those fall into "disassemble all the things" category. Ciro also does "standards dissection" and "a new version of the standard is out" answers, but those are boring:
- What does "static" mean in a C program?
- In C++ source, what is the effect of
extern "C"? - Char array vs Char Pointer in C
- How to compile glibc from source and use it?
- When should
static_cast,dynamic_cast,const_castandreinterpret_castbe used? - What exactly is
std::atomicin C++?. This answer was originally more appropriately entitled "Let's disassemble some stuff", and got three downvotes, so Ciro changed it to a more professional title, and it started getting upvotes. People judge books by their covers. notmain.o 0000000000000000 0000000000000017 W MyTemplate<int>::f(int) main.o 0000000000000000 0000000000000017 W MyTemplate<int>::f(int)Code 1.. From: What is explicit template instantiation in C++ and when to use it?nmoutputs showing that objects are redefined multiple times across files if you don't use template instantiation properly
- IEEE 754
- What is difference between quiet NaN and signaling NaN?
- In Java, what does NaN mean?
Without subnormals: +---+---+-------+---------------+-------------------------------+ exponent | ? | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | +---+---+-------+---------------+-------------------------------+ | | | | | | v v v v v v ----------------------------------------------------------------- floats * **** * * * * * * * * * * * * ----------------------------------------------------------------- ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ | | | | | | 0 | 2^-126 2^-125 2^-124 2^-123 | 2^-127 With subnormals: +-------+-------+---------------+-------------------------------+ exponent | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | +-------+-------+---------------+-------------------------------+ | | | | | v v v v v ----------------------------------------------------------------- floats * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * ----------------------------------------------------------------- ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ | | | | | | 0 | 2^-126 2^-125 2^-124 2^-123 | 2^-127Code 2.Visualization of subnormal floating point numbers vs what IEEE 754 would look like without them. From: What is a subnormal floating point number?
- Computer science
- Algorithms
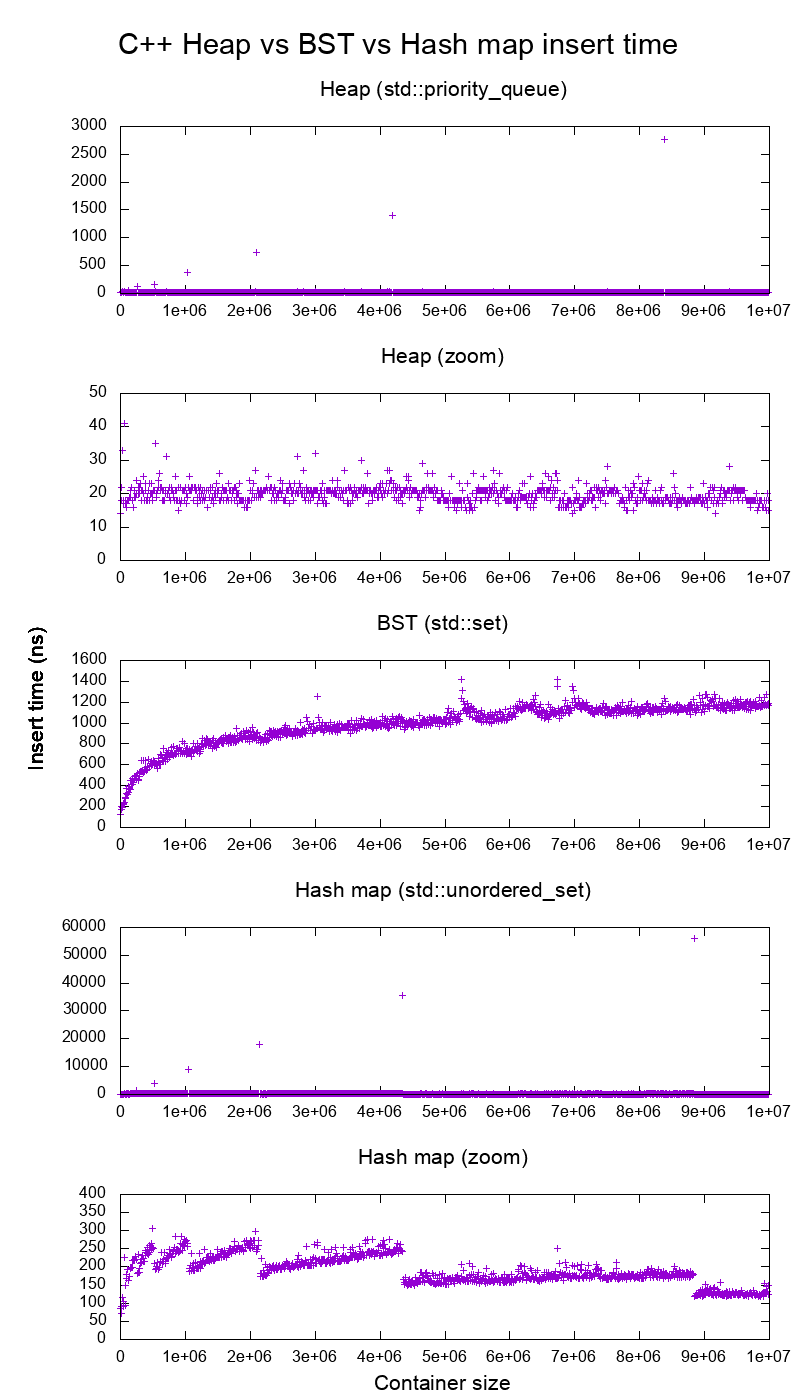
Figure 5. Average insertion time into heaps, binary search tree and hash maps of the C++ standard library. Source. From: Heap vs Binary Search Tree (BST)
- Is it necessary for NP problems to be decision problems?
- Polynomial time and exponential time. Answered focusing on the definition of "exponential time".
- What is the smallest Turing machine where it is unknown if it halts or not?. Answer focusing on "blank tape" initial condition only. Large parts of it are summarizing the Busy Beaver Challenge, but some additions were made.
- Algorithms
- Git
| 0 | 4 | 8 | C | |-------------|--------------|-------------|----------------| 0 | DIRC | Version | File count | ctime ...| 0 | ... | mtime | device | 2 | inode | mode | UID | GID | 2 | File size | Entry SHA-1 ...| 4 | ... | Flags | Index SHA-1 ...| 4 | ... |Code 3.ASCII art depicting the binary file format of the Git index file. From: What does the git index contain EXACTLY?tree {tree_sha} {parents} author {author_name} <{author_email}> {author_date_seconds} {author_date_timezone} committer {committer_name} <{committer_email}> {committer_date_seconds} {committer_date_timezone} {commit message}Code 4.Description of the Git commit object binary data structure. From: What is the file format of a git commit object data structure?- How do I clone a subdirectory only of a Git repository?
- Python
- Web technology
- OpenGL
Figure 7. OpenGL rendering output dumped to a GIF file. Source. From: How to use GLUT/OpenGL to render to a file?- What are shaders in OpenGL?
- Why do we use 4x4 matrices to transform things in 3D?
Figure 10. Sinusoidal circular wave heatmap generated with an OpenGL shader at 60 FPS on SDL. Source.
- Node.js
- Ruby on Rails
- POSIX
- What is POSIX? Huge classified overview of the most important things that POSIX specifies.
- Systems programming
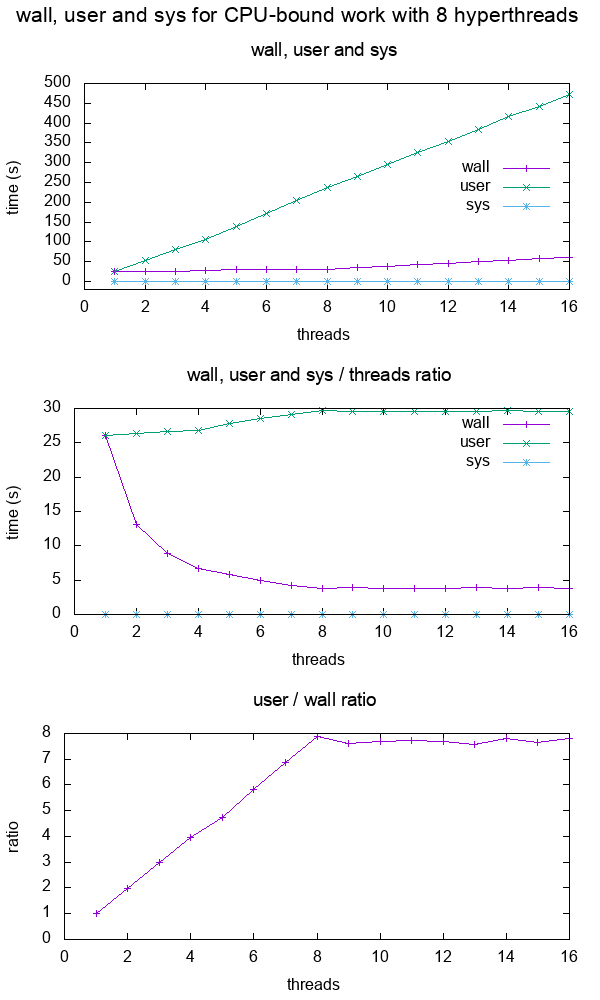
- What do the terms "CPU bound" and "I/O bound" mean?
Figure 12. Plot of "real", "user" and "sys" mean times of the output of time for CPU-bound workload with 8 threads. Source. From: What do 'real', 'user' and 'sys' mean in the output of time?+--------+ +------------+ +------+ | device |>---------------->| function 0 |>----->| BAR0 | | | | | +------+ | |>------------+ | | | | | | | +------+ ... ... | | |>----->| BAR1 | | | | | | +------+ | |>--------+ | | | +--------+ | | ... ... ... | | | | | | | | +------+ | | | |>----->| BAR5 | | | +------------+ +------+ | | | | | | +------------+ +------+ | +--->| function 1 |>----->| BAR0 | | | | +------+ | | | | | | +------+ | | |>----->| BAR1 | | | | +------+ | | | | ... ... ... | | | | | | +------+ | | |>----->| BAR5 | | +------------+ +------+ | | | ... | | | +------------+ +------+ +------->| function 7 |>----->| BAR0 | | | +------+ | | | | +------+ | |>----->| BAR1 | | | +------+ | | ... ... ... | | | | +------+ | |>----->| BAR5 | +------------+ +------+Code 5.Logical struture PCIe device, functions and BARs. From: What is the Base Address Register (BAR) in PCIe?
- Electronics
- Raspberry Pi
Figure 13. Raspberry Pi 2 directly connected to a laptop with an Ethernet cable. Image from answer to: How to hook up a Raspberry Pi via Ethernet to a laptop without a router?Figure 14. . Image from answer to: How to hook up a Raspberry Pi via Ethernet to a laptop without a router? Figure 15. . Image from answer to: How to emulate the Raspberry Pi 2 on QEMU? Figure 16. Bare metal LED blinker program running on a Raspberry Pi 2. Image from answer to: How to run a C program with no OS on the Raspberry Pi?
- Raspberry Pi
- Computer security
- Media
Video 2. Canon in D in C. Source.The original question was deleted, lol...: How to programmatically synthesize music?- How to resize a picture using ffmpeg's sws_scale()?
- Is there any decent speech recognition software for Linux? ran a few examples manually on
vosk-apiand compared to ground truth.
- Eclipse
- Computer hardware
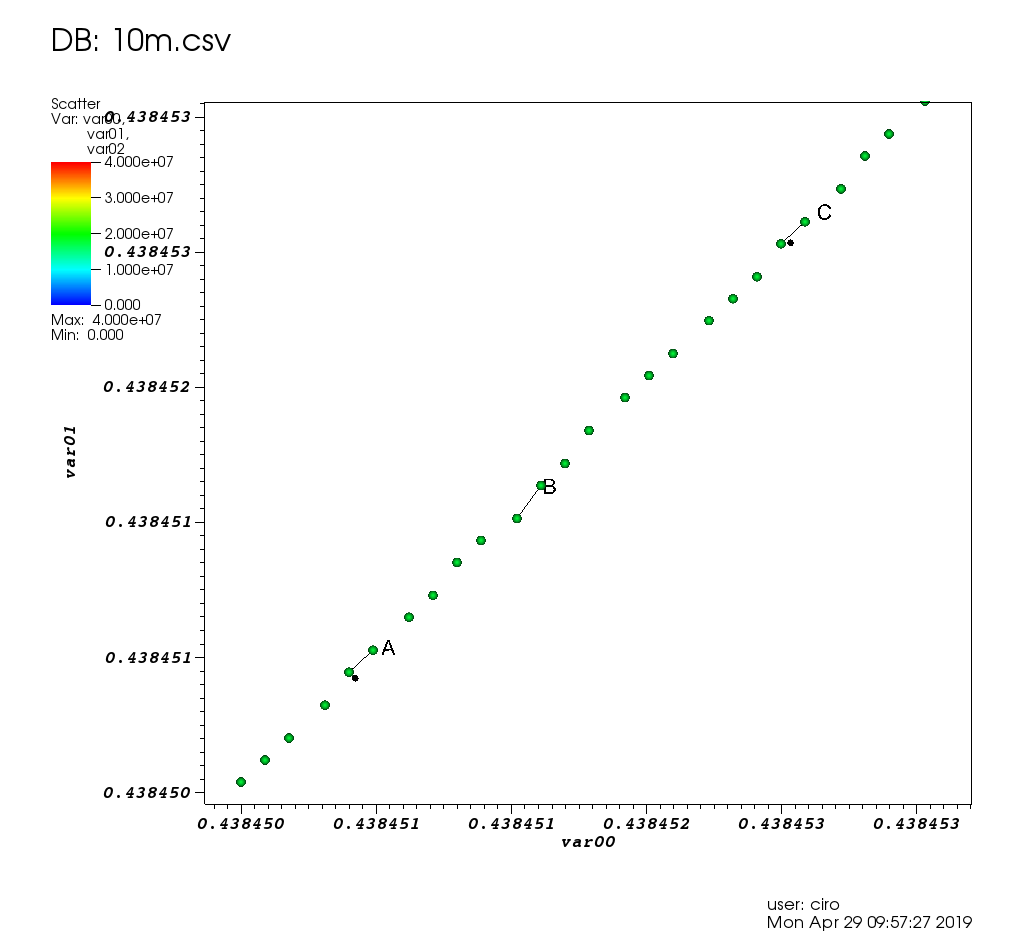
- Scientific visualization software
Figure 17. VisIt zoom in 10 million straight line plot with some manually marked points. Source. From: Section "Survey of open source interactive plotting software with a 10 million point scatter plot benchmark by Ciro Santilli"
- Numerical analysis
- Computational physics
- Register transfer level languages like Verilog and VHDL
- Verilog:
Figure 19. . See also: Section "Verilator interactive example"
- Verilog:
- Android
Video 4. Android screen showing live on an Ubuntu laptop through ADB. Source. From: How to see the Android screen live on an Ubuntu desktop through ADB?
- Debugging
- Program optimization
- What is tail call optimization?
Figure 21. . Source. The answer compares gprof, valgrind callgrind, perf and gperftools on a single simple executable.
- Data
Figure 22. Mathematics dump of Wikipedia CatTree. Source. In this project, Ciro Santilli explored extracting the category and article tree out of the Wikipedia dumps.
- Mathematics
Figure 23. Diagram of the fundamental theorem on homomorphisms by Ciro Santilli (2020)Shows the relationship between group homomorphisms and normal subgroups.- Section "Formalization of mathematics": some early thoughts that could be expanded. Ciro almost had a stroke when he understood this stuff in his teens.
Figure 24. Simple example of the Discrete Fourier transform. Source. That was missing from Wikipedia page: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Discrete_Fourier_transform!
- Network programming
- Physics
- What is the difference between plutonium and uranium?
Figure 25. Spacetime diagram illustrating how faster-than-light travel implies time travel. From: Does faster than light travel imply travelling back in time?
- Biology
Figure 26. Top view of an open Oxford Nanopore MinION. Source. From: Section "How to use an Oxford Nanopore MinION to extract DNA from river water and determine which bacteria live in it"Figure 27. Mass fractions in a minimal growth medium vs an amino acid cut in a simulation of the E. Coli Whole Cell Model by Covert Lab. Source. From: Section "E. Coli Whole Cell Model by Covert Lab"
- Quantum computing
- Section "Quantum computing is just matrix multiplication"
Figure 28. Visualization of the continuous deformation of states as we walk around the Bloch sphere represented as photon polarization arrows. From: Understanding the Bloch sphere.
- Bitcoin
- GIMP
Figure 29. GIMP screenshot part of how to combine two images side-by-side in GIMP?
- Home DIY
Figure 30. Total_Blackout_Cassette_Roller_Blind_With_Curtains.Source. From: Section "How to blackout your window without drilling"
- China
E. Coli Whole Cell Model by Covert Lab Condition Updated 2025-07-16
reconstruction/ecoli/flat/condition/nutrient/minimal.tsvcontains the nutrients in a minimal environment in which the cell survives:If we compare that to"molecule id" "lower bound (units.mmol / units.g / units.h)" "upper bound (units.mmol / units.g / units.h)" "ADP[c]" 3.15 3.15 "PI[c]" 3.15 3.15 "PROTON[c]" 3.15 3.15 "GLC[p]" NaN 20 "OXYGEN-MOLECULE[p]" NaN NaN "AMMONIUM[c]" NaN NaN "PI[p]" NaN NaN "K+[p]" NaN NaN "SULFATE[p]" NaN NaN "FE+2[p]" NaN NaN "CA+2[p]" NaN NaN "CL-[p]" NaN NaN "CO+2[p]" NaN NaN "MG+2[p]" NaN NaN "MN+2[p]" NaN NaN "NI+2[p]" NaN NaN "ZN+2[p]" NaN NaN "WATER[p]" NaN NaN "CARBON-DIOXIDE[p]" NaN NaN "CPD0-1958[p]" NaN NaN "L-SELENOCYSTEINE[c]" NaN NaN "GLC-D-LACTONE[c]" NaN NaN "CYTOSINE[c]" NaN NaNreconstruction/ecoli/flat/condition/nutrient/minimal_plus_amino_acids.tsv, we see that it adds the 20 amino acids on top of the minimal condition:so we guess that"L-ALPHA-ALANINE[p]" NaN NaN "ARG[p]" NaN NaN "ASN[p]" NaN NaN "L-ASPARTATE[p]" NaN NaN "CYS[p]" NaN NaN "GLT[p]" NaN NaN "GLN[p]" NaN NaN "GLY[p]" NaN NaN "HIS[p]" NaN NaN "ILE[p]" NaN NaN "LEU[p]" NaN NaN "LYS[p]" NaN NaN "MET[p]" NaN NaN "PHE[p]" NaN NaN "PRO[p]" NaN NaN "SER[p]" NaN NaN "THR[p]" NaN NaN "TRP[p]" NaN NaN "TYR[p]" NaN NaN "L-SELENOCYSTEINE[c]" NaN NaN "VAL[p]" NaN NaNNaNin theupper moundlikely means infinite.We can try to understand the less obvious ones:ADP: TODOPI: TODOPROTON[c]: presumably a measure of pHGLC[p]: glucose, this can be seen by comparingminimal.tsvwithminimal_no_glucose.tsvAMMONIUM: ammonium. This appears to be the primary source of nitrogen atoms for producing amino acids.CYTOSINE[c]: hmmm, why is external cytosine needed? Weird.
reconstruction/ecoli/flat/reconstruction/ecoli/flat/condition/timeseries/contains sequences of conditions for each time. For example:reconstruction/ecoli/flat/reconstruction/ecoli/flat/condition/timeseries/000000_basal.tsvcontains:which means just using"time (units.s)" "nutrients" 0 "minimal"reconstruction/ecoli/flat/condition/nutrient/minimal.tsvuntil infinity. That is the default one used byrunSim.py, as can be seen from./out/manual/wildtype_000000/000000/generation_000000/000000/simOut/Environment/attributes/nutrientTimeSeriesLabelwhich contains just000000_basal.reconstruction/ecoli/flat/reconstruction/ecoli/flat/condition/timeseries/000001_cut_glucose.tsvis more interesting and contains:so we see that this will shift the conditions half-way to a condition that will eventually kill the bacteria because it will run out of glucose and thus energy!"time (units.s)" "nutrients" 0 "minimal" 1200 "minimal_no_glucose"
Timeseries can be selected with--variant nutrientTimeSeries X Y, see also: run variants.We can use that variant with:VARIANT="condition" FIRST_VARIANT_INDEX=1 LAST_VARIANT_INDEX=1 python runscripts/manual/runSim.pyreconstruction/ecoli/flat/condition/condition_defs.tsvcontains lines of form:"condition" "nutrients" "genotype perturbations" "doubling time (units.min)" "active TFs" "basal" "minimal" {} 44.0 [] "no_oxygen" "minimal_minus_oxygen" {} 100.0 [] "with_aa" "minimal_plus_amino_acids" {} 25.0 ["CPLX-125", "MONOMER0-162", "CPLX0-7671", "CPLX0-228", "MONOMER0-155"]conditionrefers to entries inreconstruction/ecoli/flat/condition/condition_defs.tsvnutrientsrefers to entries underreconstruction/ecoli/flat/condition/nutrient/, e.g.reconstruction/ecoli/flat/condition/nutrient/minimal.tsvorreconstruction/ecoli/flat/condition/nutrient/minimal_plus_amino_acids.tsvgenotype perturbations: there aren't any in the file, but this suggests that genotype modifications can also be incorporated heredoubling time: TODO experimental data? Because this should be a simulation output, right? Or do they cheat and fix doubling by time?active TFs: this suggests that they are cheating transcription factors here, as those would ideally be functions of other more basic inputs
E. Coli Whole Cell Model by Covert Lab Default run variant Updated 2025-07-16
The default run variant, if you don't pass any options, just has the minimal growth conditions set. What this means can be seen at condition.
Notably, this implies a growth medium that includes glucose and salt. It also includes oxygen, which is not strictly required, but greatly benefits cell growth, and is of course easier to have than not have as it is part of the atmosphere!
But the medium does not include amino acids, which the bacteria will have to produce by itself.
E. Coli Whole Cell Model by Covert Lab Source code overview Updated 2025-07-16
Let's try to understand some interesting looking, with a special focus on our understanding of the tiny E. Coli K-12 MG1655 operon thrLABC part of the metabolism, which we have well understood at Section "E. Coli K-12 MG1655 operon thrLABC".
reconstruction/ecoli/flat/compartments.tsvcontains cellular compartment information:"abbrev" "id" "n" "CCO-BAC-NUCLEOID" "j" "CCO-CELL-PROJECTION" "w" "CCO-CW-BAC-NEG" "c" "CCO-CYTOSOL" "e" "CCO-EXTRACELLULAR" "m" "CCO-MEMBRANE" "o" "CCO-OUTER-MEM" "p" "CCO-PERI-BAC" "l" "CCO-PILUS" "i" "CCO-PM-BAC-NEG"CCO: "Celular COmpartment"BAC-NUCLEOID: nucleoidCELL-PROJECTION: cell projectionCW-BAC-NEG: TODO confirm: cell wall (of a Gram-negative bacteria)CYTOSOL: cytosolEXTRACELLULAR: outside the cellMEMBRANE: cell membraneOUTER-MEM: bacterial outer membranePERI-BAC: periplasmPILUS: pilusPM-BAC-NEG: TODO: plasma membrane, but that is the same as cell membrane no?
reconstruction/ecoli/flat/promoters.tsvcontains promoter information. Simple file, sample lines:corresponds to E. Coli K-12 MG1655 promoter thrLp, which starts as position 148."position" "direction" "id" "name" 148 "+" "PM00249" "thrLp"reconstruction/ecoli/flat/proteins.tsvcontains protein information. Sample line corresponding to e. Coli K-12 MG1655 gene thrA:so we understand that:"aaCount" "name" "seq" "comments" "codingRnaSeq" "mw" "location" "rnaId" "id" "geneId" [91, 46, 38, 44, 12, 53, 30, 63, 14, 46, 89, 34, 23, 30, 29, 51, 34, 4, 20, 0, 69] "ThrA" "MRVL..." "Location information from Ecocyc dump." "AUGCGAGUGUUG..." [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 89103.51099999998, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] ["c"] "EG10998_RNA" "ASPKINIHOMOSERDEHYDROGI-MONOMER" "EG10998"aaCount: amino acid count, how many of each of the 20 proteinogenic amino acid are thereseq: full sequence, using the single letter abbreviation of the proteinogenic amino acidsmw; molecular weight? The 11 components appear to be given atreconstruction/ecoli/flat/scripts/unifyBulkFiles.py:so they simply classify the weight? Presumably this exists for complexes that have multiple classes?molecular_weight_keys = [ '23srRNA', '16srRNA', '5srRNA', 'tRNA', 'mRNA', 'miscRNA', 'protein', 'metabolite', 'water', 'DNA', 'RNA' # nonspecific RNA ]23srRNA,16srRNA,5srRNAare the three structural RNAs present in the ribosome: 23S ribosomal RNA, 16S ribosomal RNA, 5S ribosomal RNA, all others are obvious:- tRNA
- mRNA
- protein. This is the seventh class, and this enzyme only contains mass in this class as expected.
- metabolite
- water
- DNA
- RNA: TODO
rnavsmiscRNA
location: cell compartment where the protein is present,cdefined atreconstruction/ecoli/flat/compartments.tsvas cytoplasm, as expected for something that will make an amino acid
reconstruction/ecoli/flat/rnas.tsv: TODO vstranscriptionUnits.tsv. Sample lines:"halfLife" "name" "seq" "type" "modifiedForms" "monomerId" "comments" "mw" "location" "ntCount" "id" "geneId" "microarray expression" 174.0 "ThrA [RNA]" "AUGCGAGUGUUG..." "mRNA" [] "ASPKINIHOMOSERDEHYDROGI-MONOMER" "" [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 790935.00399999996, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] ["c"] [553, 615, 692, 603] "EG10998_RNA" "EG10998" 0.0005264904halfLife: half-lifemw: molecular weight, same as inreconstruction/ecoli/flat/proteins.tsv. This molecule only have weight in themRNAclass, as expected, as it just codes for a proteinlocation: same as inreconstruction/ecoli/flat/proteins.tsvntCount: nucleotide count for each of the ATGCmicroarray expression: presumably refers to DNA microarray for gene expression profiling, but what measure exactly?
reconstruction/ecoli/flat/sequence.fasta: FASTA DNA sequence, first two lines:>E. coli K-12 MG1655 U00096.2 (1 to 4639675 = 4639675 bp) AGCTTTTCATTCTGACTGCAACGGGCAATATGTCTCTGTGTGGATTAAAAAAAGAGTGTCTGATAGCAGCTTCTGreconstruction/ecoli/flat/transcriptionUnits.tsv: transcription units. We can observe for example the two different transcription units of the E. Coli K-12 MG1655 operon thrLABC in the lines:"expression_rate" "direction" "right" "terminator_id" "name" "promoter_id" "degradation_rate" "id" "gene_id" "left" 0.0 "f" 310 ["TERM0-1059"] "thrL" "PM00249" 0.198905992329492 "TU0-42486" ["EG11277"] 148 657.057317358791 "f" 5022 ["TERM_WC-2174"] "thrLABC" "PM00249" 0.231049060186648 "TU00178" ["EG10998", "EG10999", "EG11000", "EG11277"] 148promoter_id: matches promoter id inreconstruction/ecoli/flat/promoters.tsvgene_id: matches id inreconstruction/ecoli/flat/genes.tsvid: matches exactly those used in BioCyc, which is quite nice, might be more or less standardized:
reconstruction/ecoli/flat/genes.tsv"length" "name" "seq" "rnaId" "coordinate" "direction" "symbol" "type" "id" "monomerId" 66 "thr operon leader peptide" "ATGAAACGCATT..." "EG11277_RNA" 189 "+" "thrL" "mRNA" "EG11277" "EG11277-MONOMER" 2463 "ThrA" "ATGCGAGTGTTG" "EG10998_RNA" 336 "+" "thrA" "mRNA" "EG10998" "ASPKINIHOMOSERDEHYDROGI-MONOMER"reconstruction/ecoli/flat/metabolites.tsvcontains metabolite information. Sample lines:In the case of the enzyme thrA, one of the two reactions it catalyzes is "L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde" into "Homoserine"."id" "mw7.2" "location" "HOMO-SER" 119.12 ["n", "j", "w", "c", "e", "m", "o", "p", "l", "i"] "L-ASPARTATE-SEMIALDEHYDE" 117.104 ["n", "j", "w", "c", "e", "m", "o", "p", "l", "i"]Starting from the enzyme page: biocyc.org/gene?orgid=ECOLI&id=EG10998 we reach the reaction page: biocyc.org/ECOLI/NEW-IMAGE?type=REACTION&object=HOMOSERDEHYDROG-RXN which has reaction IDHOMOSERDEHYDROG-RXN, and that page which clarifies the IDs:so these are the compounds that we care about.- biocyc.org/compound?orgid=ECOLI&id=L-ASPARTATE-SEMIALDEHYDE: "L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde" has ID
L-ASPARTATE-SEMIALDEHYDE - biocyc.org/compound?orgid=ECOLI&id=HOMO-SER: "Homoserine" has ID
HOMO-SER
- biocyc.org/compound?orgid=ECOLI&id=L-ASPARTATE-SEMIALDEHYDE: "L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde" has ID
reconstruction/ecoli/flat/reactions.tsvcontains chemical reaction information. Sample lines:"reaction id" "stoichiometry" "is reversible" "catalyzed by" "HOMOSERDEHYDROG-RXN-HOMO-SER/NAD//L-ASPARTATE-SEMIALDEHYDE/NADH/PROTON.51." {"NADH[c]": -1, "PROTON[c]": -1, "HOMO-SER[c]": 1, "L-ASPARTATE-SEMIALDEHYDE[c]": -1, "NAD[c]": 1} false ["ASPKINIIHOMOSERDEHYDROGII-CPLX", "ASPKINIHOMOSERDEHYDROGI-CPLX"] "HOMOSERDEHYDROG-RXN-HOMO-SER/NADP//L-ASPARTATE-SEMIALDEHYDE/NADPH/PROTON.53." {"NADPH[c]": -1, "NADP[c]": 1, "PROTON[c]": -1, "L-ASPARTATE-SEMIALDEHYDE[c]": -1, "HOMO-SER[c]": 1 false ["ASPKINIIHOMOSERDEHYDROGII-CPLX", "ASPKINIHOMOSERDEHYDROGI-CPLX"]catalized by: here we seeASPKINIHOMOSERDEHYDROGI-CPLX, which we can guess is a protein complex made out ofASPKINIHOMOSERDEHYDROGI-MONOMER, which is the ID for thethrAwe care about! This is confirmed incomplexationReactions.tsv.
reconstruction/ecoli/flat/complexationReactions.tsvcontains information about chemical reactions that produce protein complexes:The"process" "stoichiometry" "id" "dir" "complexation" [ { "molecule": "ASPKINIHOMOSERDEHYDROGI-CPLX", "coeff": 1, "type": "proteincomplex", "location": "c", "form": "mature" }, { "molecule": "ASPKINIHOMOSERDEHYDROGI-MONOMER", "coeff": -4, "type": "proteinmonomer", "location": "c", "form": "mature" } ] "ASPKINIHOMOSERDEHYDROGI-CPLX_RXN" 1coeffis how many monomers need to get together for form the final complex. This can be seen from the Summary section of ecocyc.org/gene?orgid=ECOLI&id=ASPKINIHOMOSERDEHYDROGI-MONOMER:Fantastic literature summary! Can't find that in database form there however.Aspartate kinase I / homoserine dehydrogenase I comprises a dimer of ThrA dimers. Although the dimeric form is catalytically active, the binding equilibrium dramatically favors the tetrameric form. The aspartate kinase and homoserine dehydrogenase activities of each ThrA monomer are catalyzed by independent domains connected by a linker region.
reconstruction/ecoli/flat/proteinComplexes.tsvcontains protein complex information:"name" "comments" "mw" "location" "reactionId" "id" "aspartate kinase / homoserine dehydrogenase" "" [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 356414.04399999994, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] ["c"] "ASPKINIHOMOSERDEHYDROGI-CPLX_RXN" "ASPKINIHOMOSERDEHYDROGI-CPLX"reconstruction/ecoli/flat/protein_half_lives.tsvcontains the half-life of proteins. Very few proteins are listed however for some reason.reconstruction/ecoli/flat/tfIds.csv: transcription factors information:"TF" "geneId" "oneComponentId" "twoComponentId" "nonMetaboliteBindingId" "activeId" "notes" "arcA" "EG10061" "PHOSPHO-ARCA" "PHOSPHO-ARCA" "fnr" "EG10325" "FNR-4FE-4S-CPLX" "FNR-4FE-4S-CPLX" "dksA" "EG10230"
E. Coli Whole Cell Model by Covert Lab Time series run variant Updated 2025-07-16
To modify the nutrients as a function of time, with To select a time series we can use something like:As mentioned in
python runscripts/manual/runSim.py --variant nutrientTimeSeries 25 25python runscripts/manual/runSim.py --help, nutrientTimeSeries is one of the choices from github.com/CovertLab/WholeCellEcoliRelease/blob/7e4cc9e57de76752df0f4e32eca95fb653ea64e4/models/ecoli/sim/variants/__init__.py#L5725 25 means to start from index 25 and also end at 25, so running just one simulation. 25 27 would run 25 then 26 and then 27 for example.The timeseries with index 25 is so we understand that it starts with extra amino acids in the medium, which benefit the cell, and half way through those are removed at time 1200s = 20 minutes. We would therefore expect the cell to start expressing amino acid production genes exactly at that point.
reconstruction/ecoli/flat/condition/timeseries/000025_cut_aa.tsv and contains"time (units.s)" "nutrients"
0 "minimal_plus_amino_acids"
1200 "minimal"nutrients likely means condition in that file however, see bug report with 1 1 failing: github.com/CovertLab/WholeCellEcoliRelease/issues/24When we do this the simulation ends in:so we see that the doubling time was faster than the one with minimal conditions of
Simulation finished:
- Length: 0:34:23
- Runtime: 0:08:030:42:49, which makes sense, since during the first 20 minutes the cell had extra amino acid nutrients at its disposal.The output directory now contains simulation output data under
out/manual/nutrientTimeSeries_000025/. Let's run analysis and plots for that:python runscripts/manual/analysisVariant.py &&
python runscripts/manual/analysisCohort.py --variant 25 &&
python runscripts/manual/analysisMultigen.py --variant 25 &&
python runscripts/manual/analysisSingle.py --variant 25We can now compare the outputs of this run to the default
wildtype_000000 run from Section "Install and first run".out/manual/plotOut/svg_plots/massFractionSummary.svg: because we now have two variants in the sameout/folder,wildtype_000000andnutrientTimeSeries_000025, we now see a side by side comparision of both on the same graph!The run variant where we started with amino acids initially grows faster as expected, because the cell didn't have to make it's own amino acids, so growth is a bit more efficient.
The following plots from under
out/manual/wildtype_000000/000000/{generation_000000,nutrientTimeSeries_000025}/000000/plotOut/svg_plots have been manually joined side-by-side with:for f in out/manual/wildtype_000000/000000/generation_000000/000000/plotOut/svg_plots/*; do
echo $f
svg_stack.py \
--direction h \
out/manual/wildtype_000000/000000/generation_000000/000000/plotOut/svg_plots/$(basename $f) \
out/manual/nutrientTimeSeries_000025/000000/generation_000000/000000/plotOut/svg_plots/$(basename $f) \
> tmp/$(basename $f)
doneAmino acid counts
. Source. aaCounts.svg:- default: quantities just increase
- amino acid cut: there is an abrupt fall at 20 minutes when we cut off external supply, presumably because it takes some time for the cell to start producing its own
External exchange fluxes of amino acids
. Source. aaExchangeFluxes.svg:- default: no exchanges
- amino acid cut: for all graphs except phenylalanine (PHE), either the cell was intaking the AA (negative flux), and that intake goes to 0 when the supply is cut, or the flux is always 0.
mRNA count of highly expressed mRNAs
. Source. From file expression_rna_03_high.svg. Each of the entries is a gene using the conventional gene naming convention of xyzW, e.g. here's the BioCyc for the first entry, tufA: biocyc.org/gene?orgid=ECOLI&id=EG11036, which comments Elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) is the most abundant protein in E. coli.
External exchange fluxes
. Source. mediaExcange.svg: this one is similar to aaExchangeFluxes.svg, but it also tracks other substances. The color version makes it easier to squeeze more substances in a given space, but you lose the shape of curves a bit. The title seems reversed: red must be excretion, since that's where glucose (GLC) is.The substances are different between the default and amino acid cut graphs, they seem to be the most exchanged substances. On the amino cut graph, first we see the cell intaking most (except phenylalanine, which is excreted for some reason). When we cut amino acids, the uptake of course stops.
Key mitochondrial proteins aren't necessarily in mtDNA Updated 2025-07-16
This isn't completely surprising, since when mitochondria die, their DNA is kind of left in the cell, so it is not hard to imagine how genes end up getting uptaken by the nucleus. This is suggested at Power, Sex, Suicide by Nick Lane (2006) page 196.
A limiting factor appears to be that you can't just past those genes in the nucleus, further mutations are necessary for mitochondrial protein import to work, apparenty some kind of tagging with extra amino acids.
However, you likely don't want to remove all genes from the mitochondria because mitochondria have DNA because they need to be controlled individually.
Mitochondrial protein import Updated 2025-07-16
The process that imports proteins encoded in the nuclear DNA and made in the cytosol into the mitochondria.
Power, Sex, Suicide by Nick Lane (2006) suggests that proteins are somehow tagged with extra amino acids for this.
Mycoplasma genitalium Updated 2025-07-16
www.lgcstandards-atcc.org/products/all/49896.aspx:
- £355.00 in 2019
- biosafety level: 2
Reproduction time: www.quora.com/unanswered/How-long-do-Mycoplasma-bacteria-take-to-reproduce-under-optimal-conditions
Has one of the smallest genomes known, and JCVI made a minimized strain with 473 genes: JCVI-syn3.0.
The reason why genitalium has such a small genome is that parasites tend to have smaller DNAs. So it must be highlighted that genitalium can only survive in highly enriched environments, it can't even make its own amino acids, which it normally obtains fromthe host cells! And because it cannot do cellular respiration, it very likely replicates slower than say E. Coli. It's easy to be small in such scenarios!
Power, Sex, Suicide by Nick Lane (2006) section "How to lose the cell wall without dying" page 184 has some related mentions puts it well very:
One group, the Mycoplasma, comprises mostly parasites, many of which live inside other cells. Mycoplasma cells are tiny, with very small genomes. M. genitalium, discovered in 1981, has the smallest known genome of any bacterial cell, encoding fewer than genes. Despite its simplicity, it ranks among the most common of sexually transmitted diseases, producing symptoms similar to Chlamydia infection. It is so small (less than a third of a micron in diameter, or an order of magnitude smaller than most bacteria) that it must normally be viewed under the electron microscope; and difficulties culturing it meant its significance was not appreciated until the important advances in gene sequencing in the early 1990s. Like Rickettsia, Mycoplasma have lost virtually all the genes required for making nucleotides, amino acids, and so forth. Unlike Rickettsia, however, Mycoplasma have also lost all the genes for oxygen respiration, or indeed any other form of membrane respiration: they have no cytochromes, and so must rely on fermentation for energy.
Downsides mentioned at youtu.be/PSDd3oHj548?t=293:
- too small to see on light microscope
- difficult to genetically manipulate. TODO why?
- less literature than E. Coli.
Data:
- www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/97 contains genome, genes, proteins.
- www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?mge01100 all known pathways. TODO: numerical reaction coefficients? Which enzyimes mediate what? Appears to factor pathways across organisms, which is awesome.
Parasites tend to have smaller DNAs Updated 2025-07-16
If you live in the relatively food abundant environment of another cell, then you don't have to be able to digest every single food source in existence, of defend against a wide range of predators.
So because DNA replication is a key limiting factor of bacterial replication time, you just reduce your genome to a minimum.
Power, Sex, Suicide by Nick Lane (2006) section "Gene loss as an evolutionary trajectory" puts it well:and also section "How to lose the cell wall without dying" page 184 has some related mentions:
One of the most extreme examples of gene loss is Rickettsia prowazekii, the cause of typhus. [...] Over evolutionary time Rickettsia has lost most of its genes, and now has a mere protein-coding genes left. [...] Rickettsia is a tiny bacterium, almost as small as a virus, which lives as a parasite inside other cells. It is so well adapted to this lifestyle that it can no longer survive outside its host cells. [...] It was able to lose most of its genes in this way simply because they were not needed: life inside other cells, if you can survive there at all, is a spoonfed existence.
While many types of bacteria do lose their cell wall during parts of their life cycle only two groups of prokaryotes have succeeded in losing their cell walls permanently, yet lived to tell the tale. It's interesting to consider the extenuating circumstances that permitted them to do so.[...]One group, the Mycoplasma, comprises mostly parasites, many of which live inside other cells. Mycoplasma cells are tiny, with very small genomes. M. genitalium, discovered in 1981, has the smallest known genome of any bacterial cell, encoding fewer than 500 genes. M. genitalium, discovered in 1981, has the smallest known genome of any bacterial cell, encoding fewer than 500 genes. [...] Like Rickettsia, Mycoplasma have lost virtually all the genes required for making nucleotides, amino acids, and so forth.
Sequence alignment Updated 2025-07-16
Sequence alignment is trying to match a DNA or amino acid sequence, even though the sequences might not be exactly the same, otherwise it would be a straight up string-search algorithm.
This is fundamental in bioinformatics for two reasons:
- when you sequence the DNA of a new species, you can guess what each protein does by comparing it with similar proteins in other species that you have already studied
- when doing DNA sequencing, and specially short-read DNA sequencing, you generally need to align the reads to reference genomes to know where you are inside the entire genome, and then be able to spot mutations, notably single-nucleotide polymorphisms